In biofertilizer production, carrier materials serve as crucial delivery media that maintain the vitality of beneficial microorganisms from the laboratory to the field. Their core function is to protect microorganisms, facilitate their survival and reproduction, and ensure effective colonization in the soil after application. Based on differences in sources and characteristics, carrier materials for biofertilizers are mainly divided into four categories, each with unique advantages and application scenarios. Meanwhile, the selection of carrier materials in 2026 will continue to focus on sustainability and functional optimization, guiding the development direction of carrier material applications.
Soil-based and mineral carriers are preferred for their cost-effectiveness and wide availability in various regions. Peat, with its high organic matter content and excellent water-holding capacity, has historically been the most widely used carrier globally. Clays and minerals are another important subgroup, including kaolin, bentonite, vermiculite, perlite, zeolite, and diatomaceous earth. These materials are frequently used due to their moisture absorption capacity and ability to maintain air permeability, creating a suitable microenvironment for microorganisms. Coal-based carriers such as lignite and charcoal (or biochar) feature porous structures, which can shield microorganisms from desiccation and environmental stress, extending their survival period.
Plant-based materials and agricultural by-products are organic carriers that can often serve as nutrient sources for microorganisms during storage. Common types include grains and husks, such as rice husks, wheat bran, rice bran, corn cobs, and sesame bran, which are rich in organic nutrients and widely available as agricultural wastes. Sugarcane by-products, including bagasse, sugarcane rind, and filter cake from sugar mills, also have good application value due to their loose structure and nutrient content. Other plant wastes like sawdust, coco peat (coconut coir), banana peel powder, and straw are also widely used as carrier materials, realizing the resource utilization of agricultural wastes while providing a favorable habitat for microorganisms.
Polymer and synthetic carriers are mainly used for embedding microorganisms, which can protect them from toxic compounds and provide a controlled-release mechanism. Natural polymers are widely used due to their biocompatibility, with alginate (most commonly used for microsphere preparation), chitosan, carrageenan, and agar being typical representatives. Synthetic or modified polymers, such as carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), polyacrylamide gel, and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) patches, have adjustable physical and chemical properties. They can be tailored according to specific production needs to optimize the protection effect and release rate of microorganisms, making them suitable for specialized biofertilizer formulations.
Organic wastes and manures are also important sources of carrier materials for biofertilizers. Compost and vermicompost are mature organic carriers formed through microbial decomposition, which not only have good water-holding and nutrient-providing capabilities but also are environmentally friendly. Animal manures, especially poultry manure and cattle manure, after proper treatment, can serve as effective carriers. Industrial sludges, such as wastewater sludge and biogas slurry, are also usable carrier materials after harmless treatment, realizing the recycling of industrial wastes.
Looking ahead to 2026, the ideal carrier materials will still prioritize chemical stability, non-toxicity to both plants and microorganisms, ease of sterilization (via autoclaving or gamma-ray irradiation), and high water-holding capacity. Notably, biochar and other carriers are increasingly favored as sustainable alternatives to non-renewable peat, aligning with the global trend of green agriculture. In summary, the carrier materials used in biofertilizer production are diverse and versatile. The rational selection of carrier materials based on production needs and environmental requirements is crucial to improving the quality and application effect of biofertilizers.
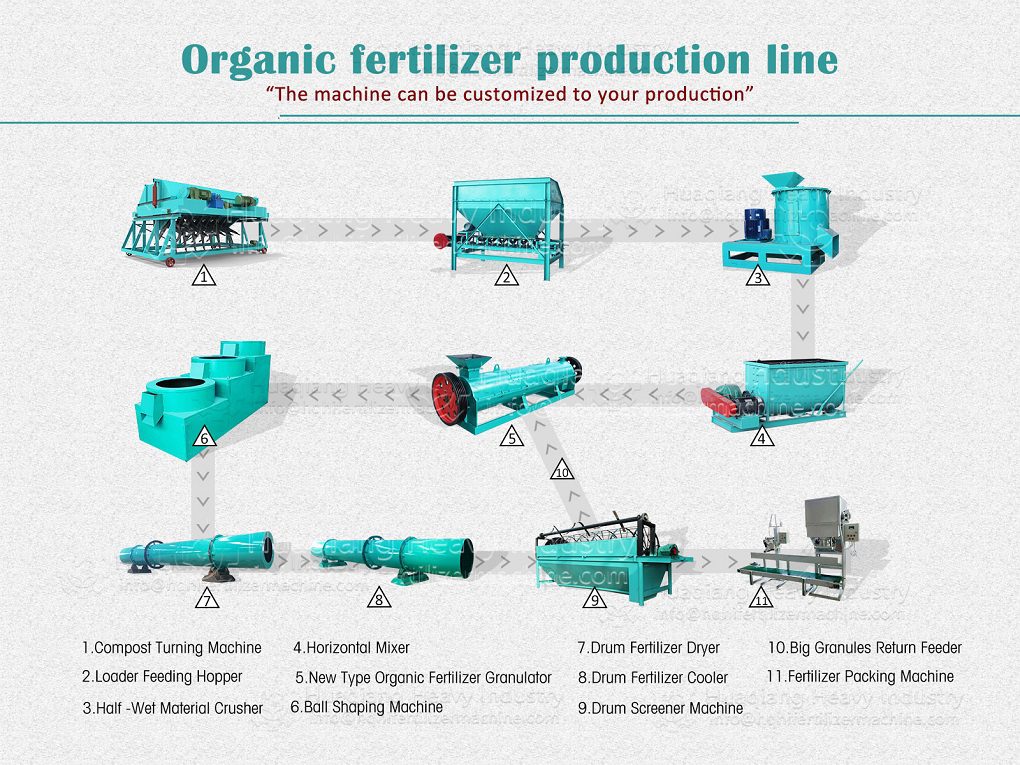
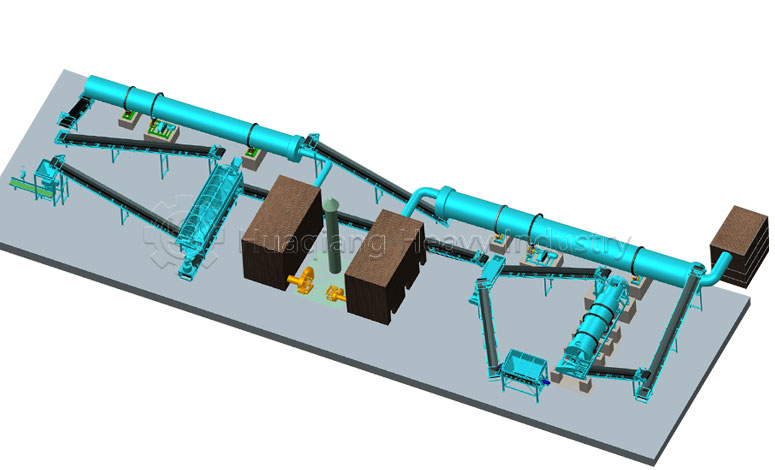
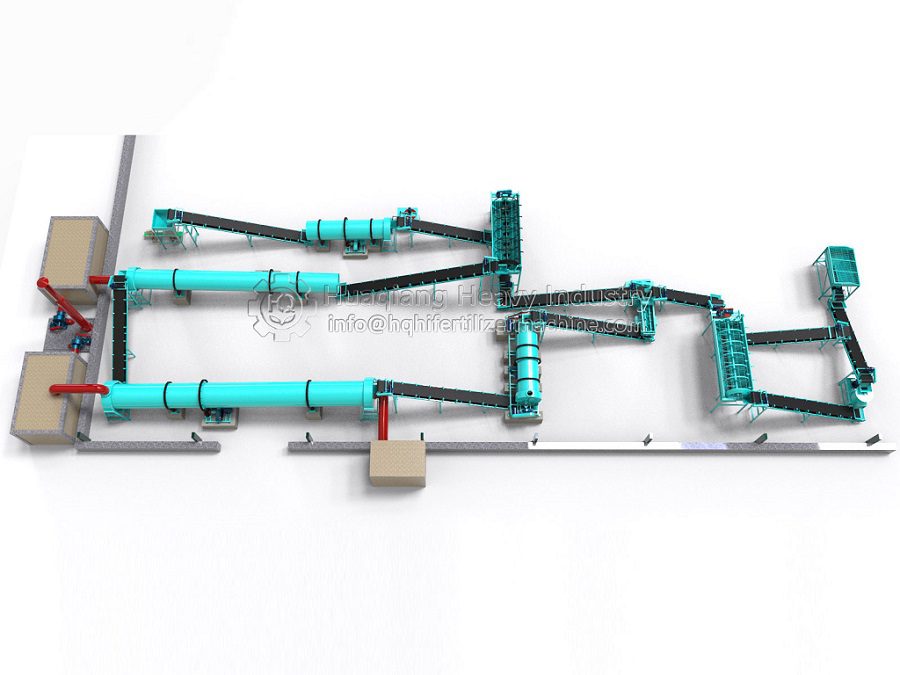
Granulation Systems for Carrier-Based Biofertilizers
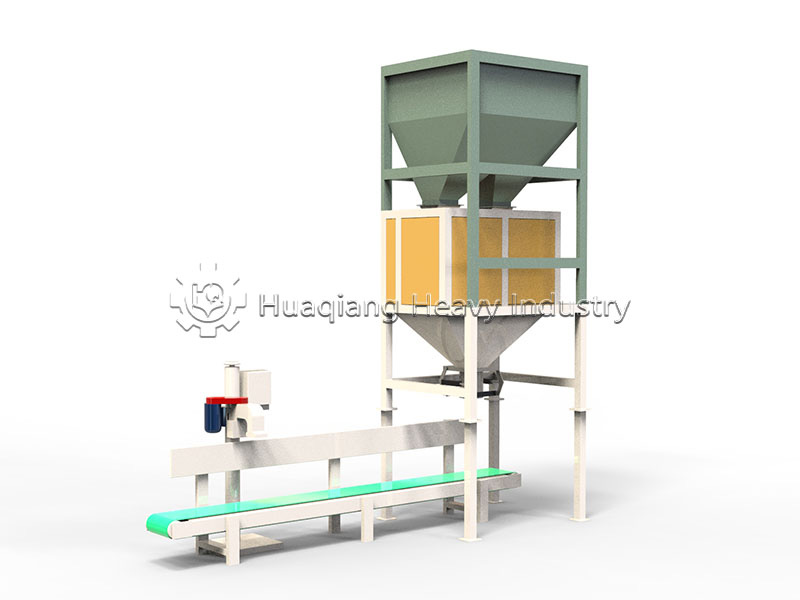
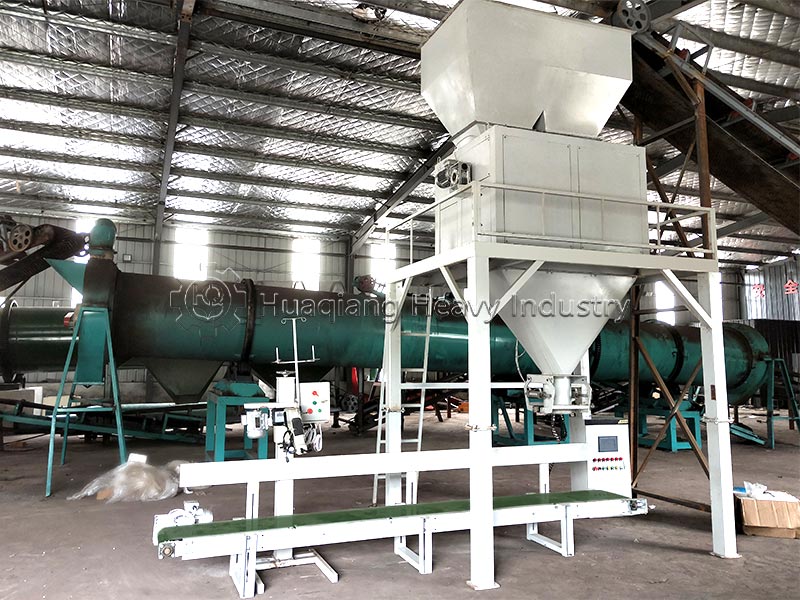
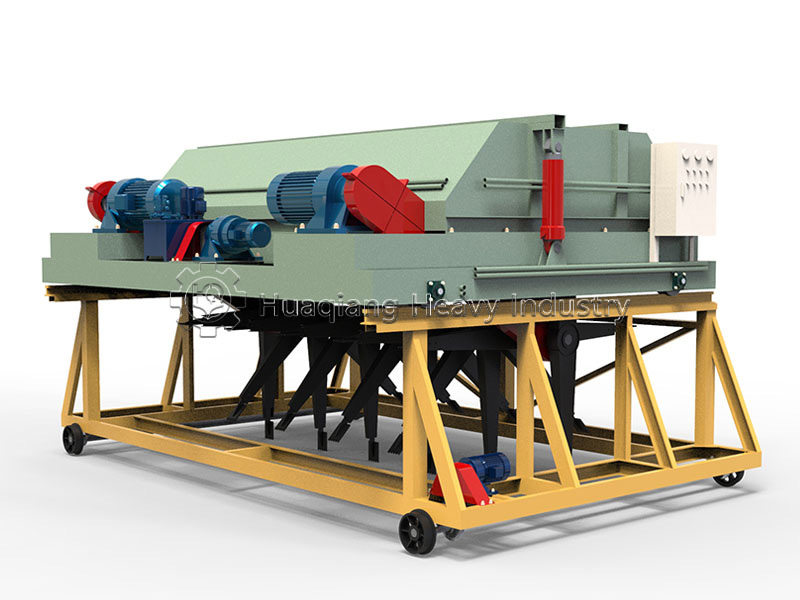
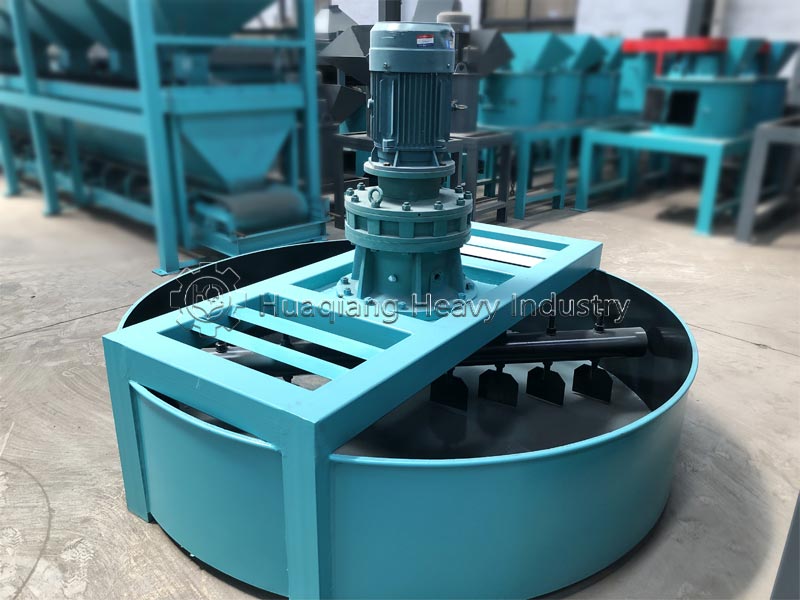
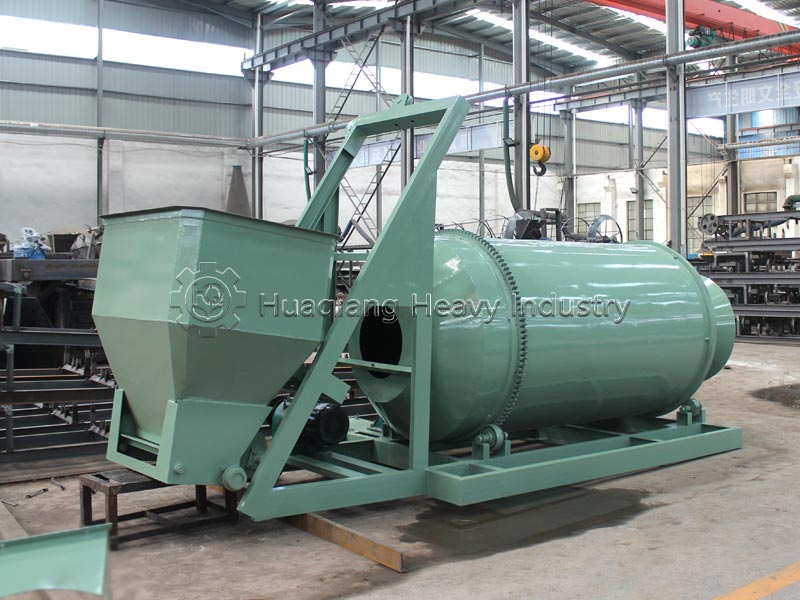
The selected carrier material, often pre-processed using equipment like a chain compost turning machine for composting organic wastes, must be effectively shaped into a marketable product. This is achieved within a complete bio organic fertilizer production line or broader organic fertilizer manufacturing system. The stage of organic fertilizer production granulation is critical, as it must form durable granules without compromising the viability of the beneficial microbes within the carrier. Common granulation technologies include the organic fertilizer disc granulation production line, where a tumbling pan gently forms spherical pellets, and the rotary drum granulator, suitable for larger-scale continuous production.
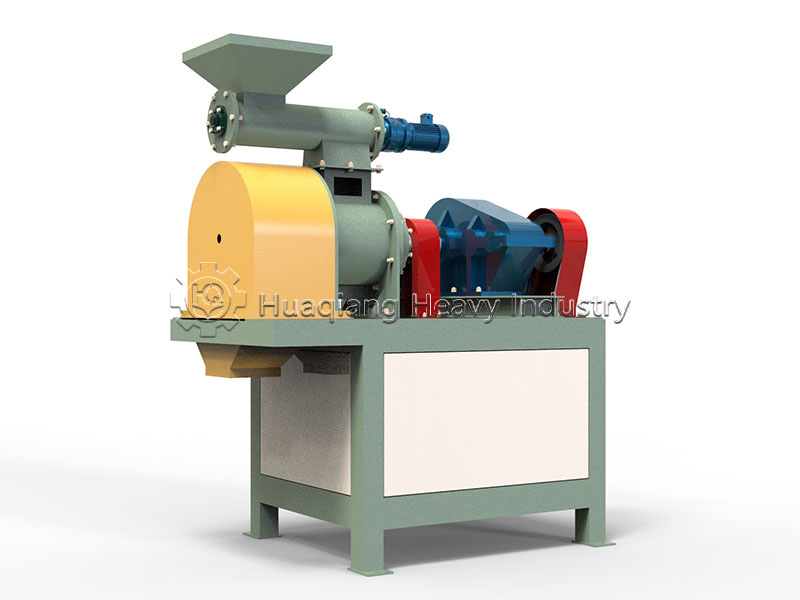
For different product specifications and production scales, alternative equipment is available. A flat die press pellet machine for sale produces dense cylindrical pellets via extrusion, while a new type two in one organic fertilizer granulator combines mixing and shaping in one unit for efficiency. More complex setups, like an organic fertilizer combined granulation production line, may integrate multiple methods. The choice of granulator, such as a specific organic fertilizer disc granulation machine, directly influences the final granule’s physical properties and its ability to protect the microbial inoculant during storage and application.
Therefore, the integration of high-quality carrier materials with appropriate, gentle granulation technology is fundamental to manufacturing effective biofertilizers. It ensures the delivery of a standardized, easy-to-apply product that successfully introduces beneficial microbes into the soil ecosystem.