In everyday use, “compostable” and “biodegradable” are often used interchangeably, but they are not equivalent. Compostable is a subcategory of biodegradable, with the core differences lying in decomposition conditions, product requirements, and applicable scenarios.
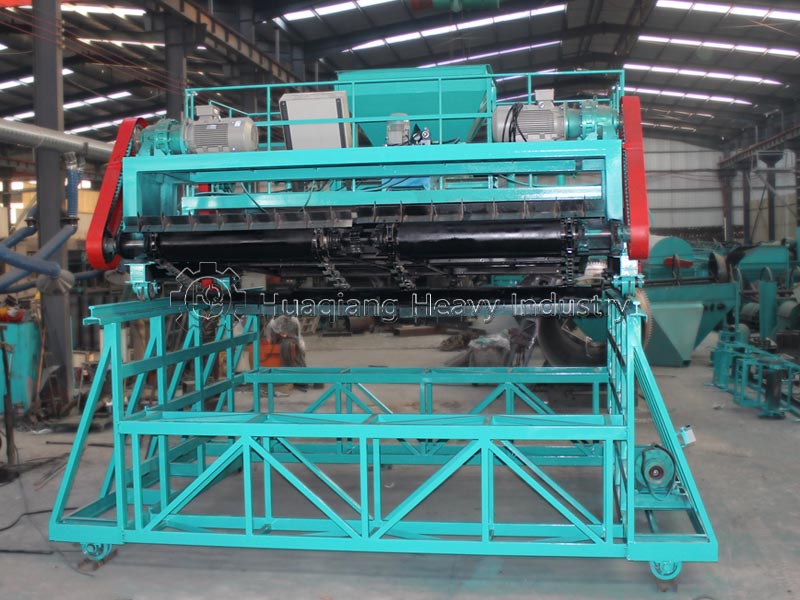
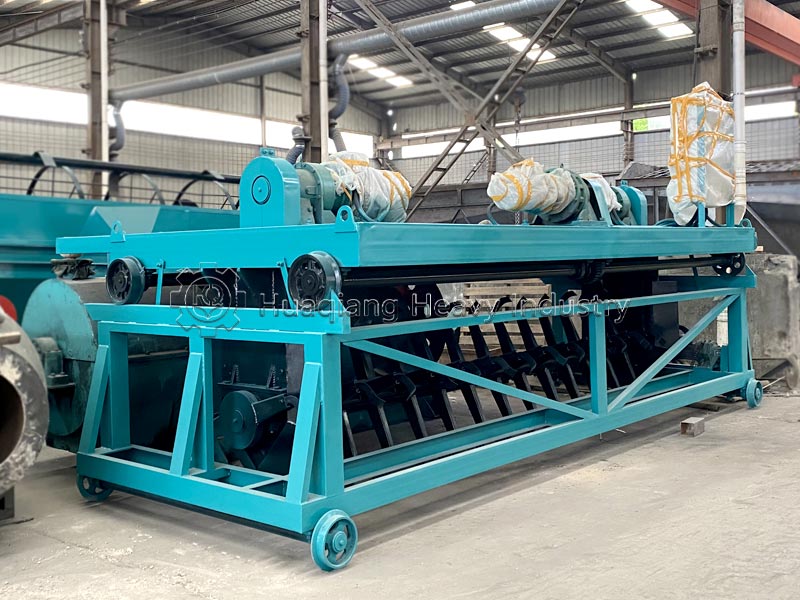
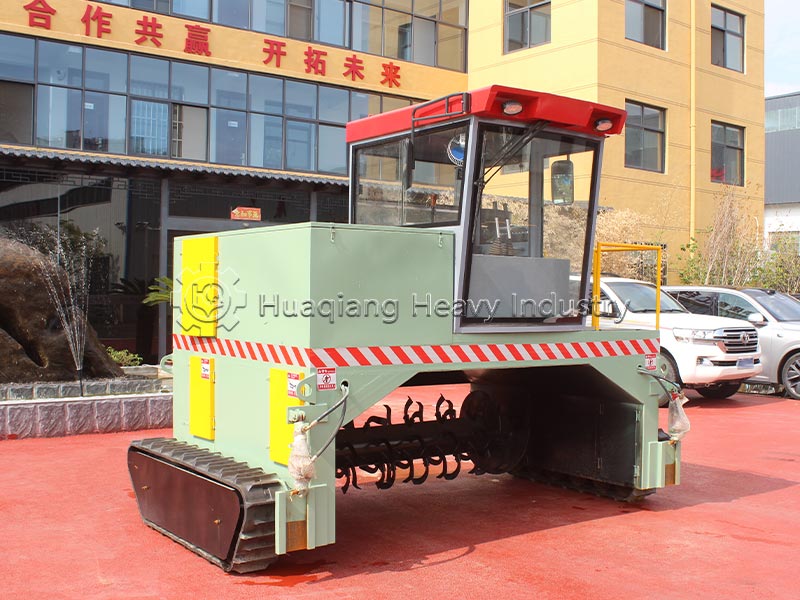
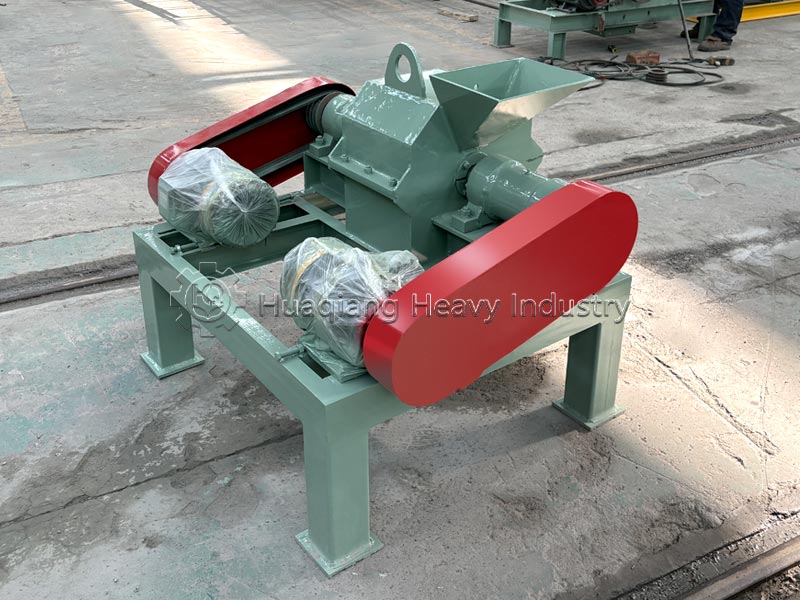
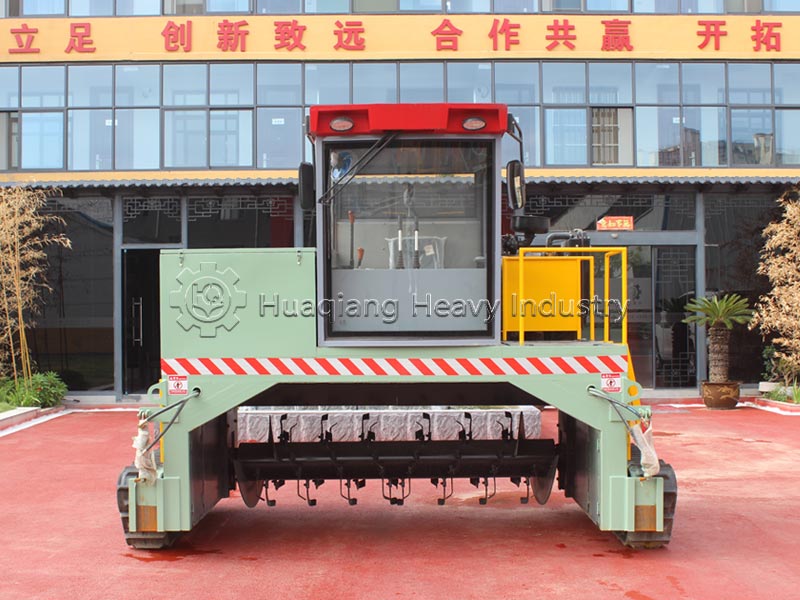
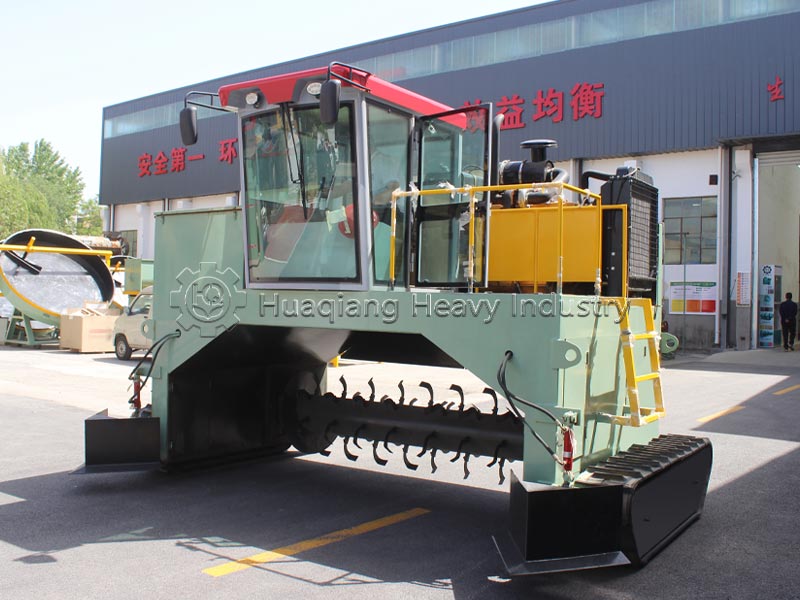
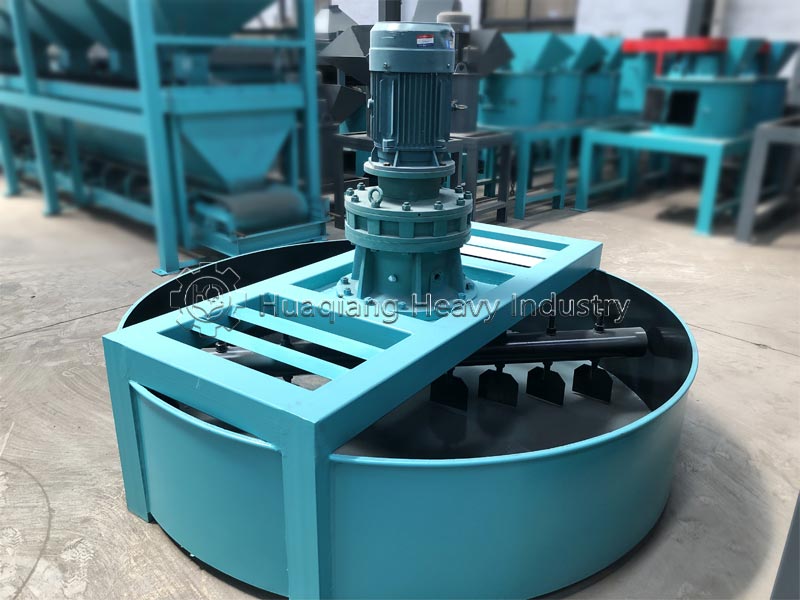
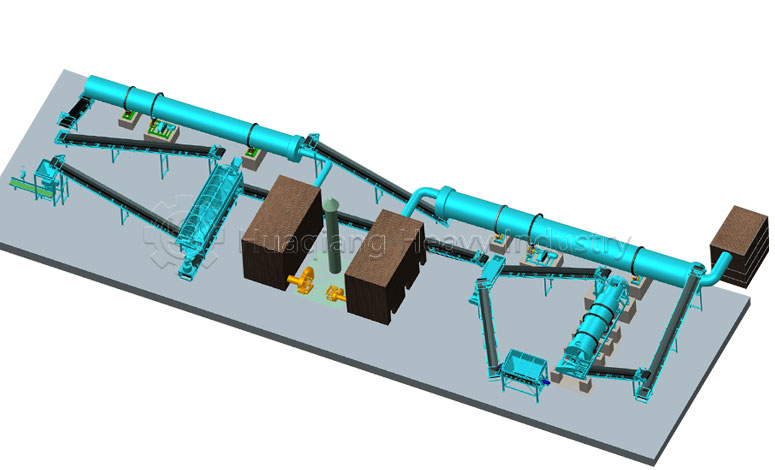
Decomposition conditions and timelines differ significantly. Biodegradable substances can be decomposed by microorganisms in the natural environment, with no strict parameter requirements, and the decomposition period varies from months to years, greatly influenced by environmental factors. Compostable substances require a specific composting environment (temperature 55-65℃, humidity 55%-60%, aerobic), and require equipment such as compost turning machines to control temperature, humidity, and aeration, achieving complete decomposition within 3-6 months; in large-scale processing, organic fertilizer production lines can precisely control parameters to ensure decomposition efficiency.
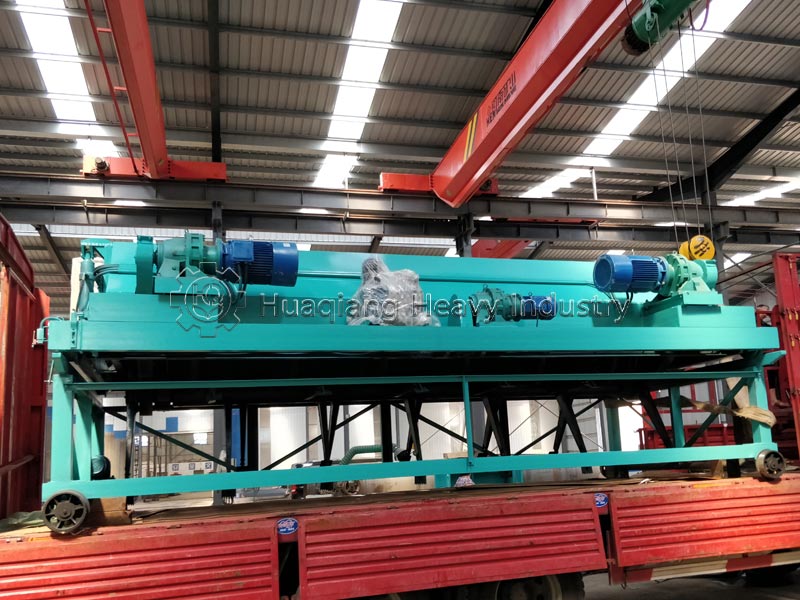

Decomposition products and standards differ. Biodegradable substances only require decomposition into water, carbon dioxide, and microorganisms, with no specific residue requirements. Compostable materials must decompose into harmless humus. After processing on an organic fertilizer production line, they can be used as organic fertilizer to improve soil and must meet environmental standards for heavy metals and other pollutants, without causing secondary pollution.
The applicable scenarios differ. Biodegradable materials have a wide range and are suitable for natural degradation scenarios; compostable materials are mostly organic waste such as kitchen waste and straw, which are standardized and processed using organic fertilizer production equipment to ultimately achieve resource utilization.
A common misconception is that not all biodegradable materials are compostable. Some materials are difficult to completely decompose in a composting environment and may even pollute the byproducts. The core difference lies in whether “complete degradation + resource utilization” can be achieved under composting conditions.