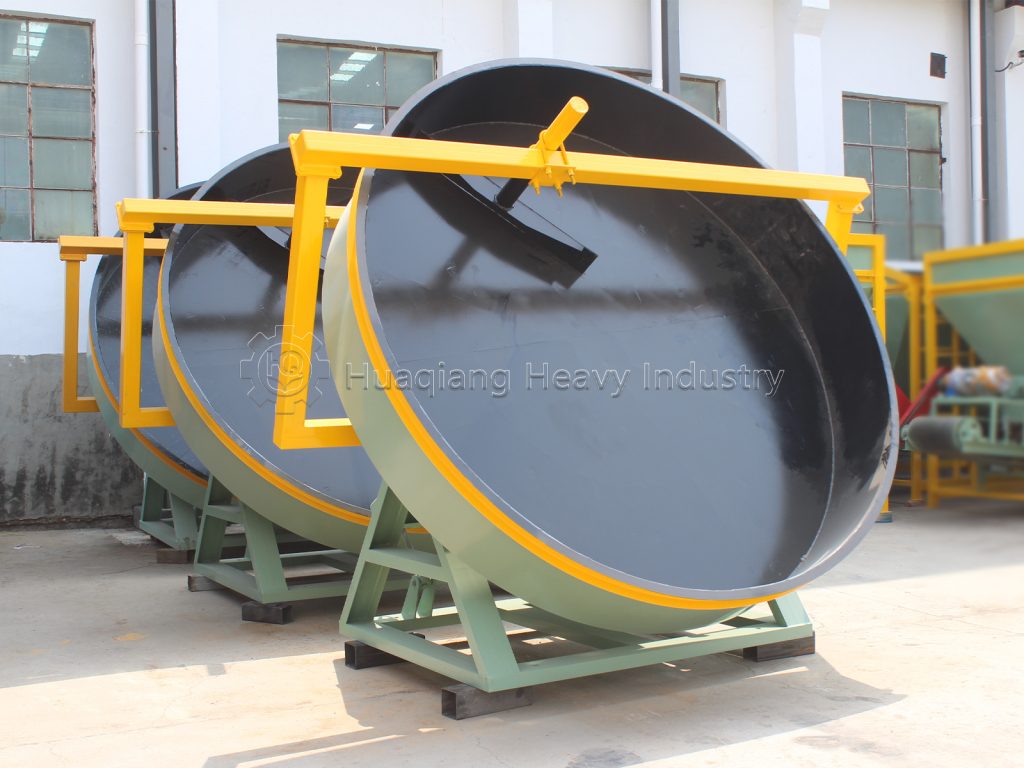
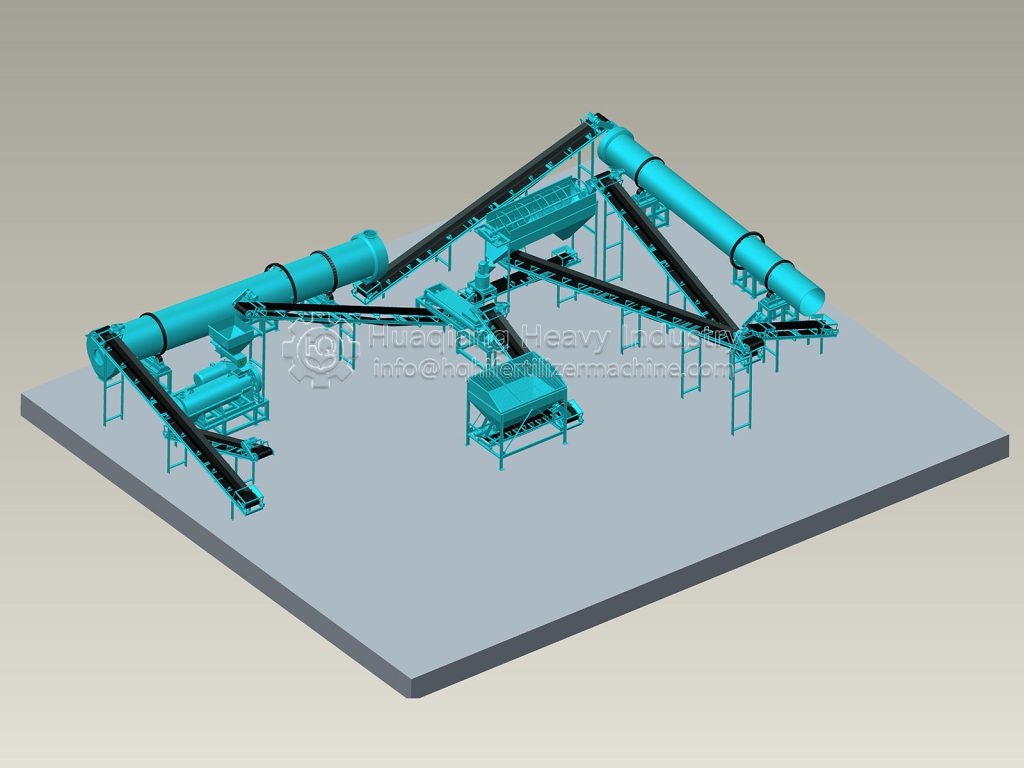
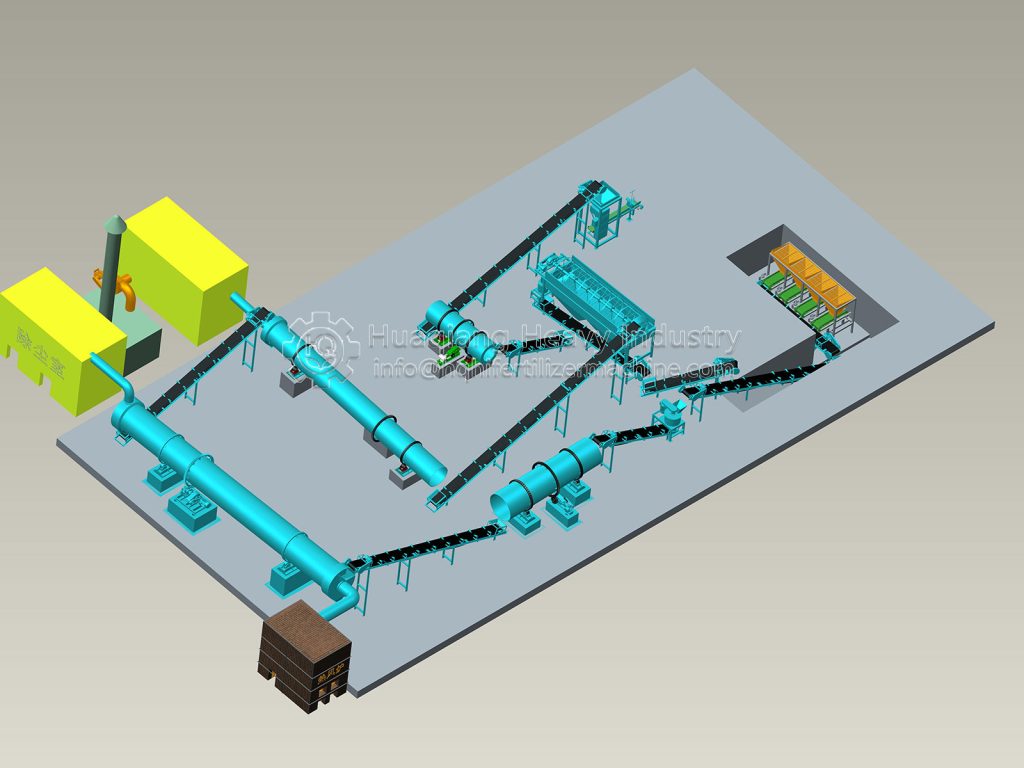
When producing compound fertilizers using a disc granulator, many factors influence granulation, such as disc diameter, disc speed, disc inclination, nozzle aperture, and moisture content. Generally speaking, disc inclination has a greater impact on the granulation rate, while disc speed has a greater influence on the compressive strength of the granules.
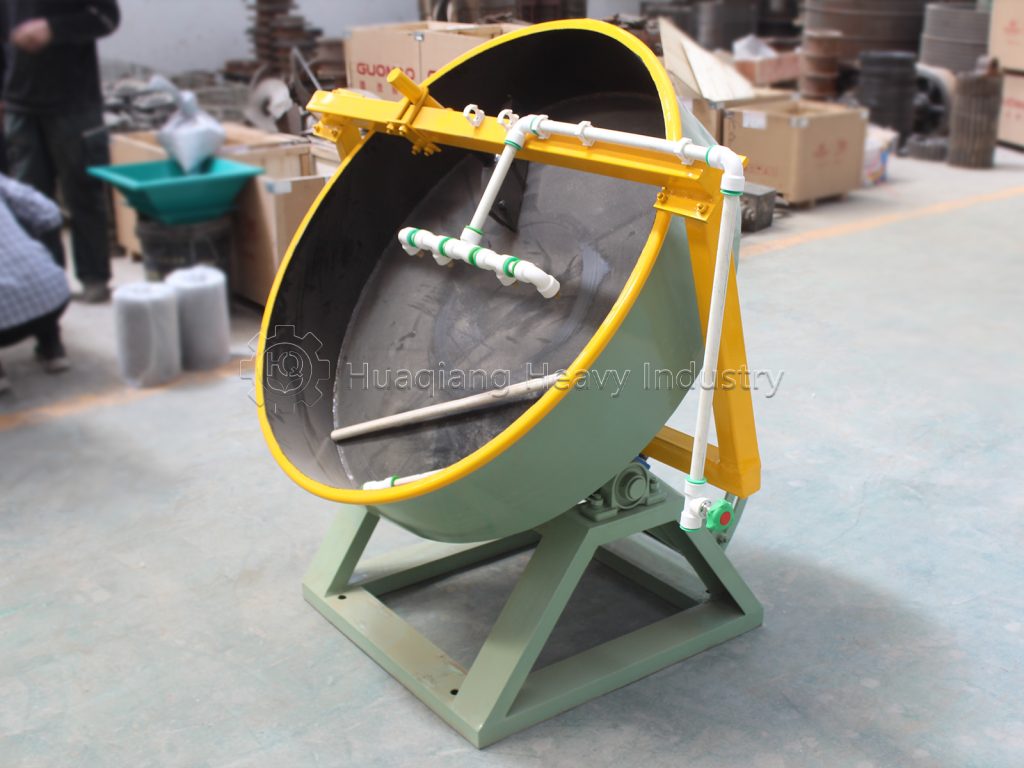

The moisture content of disc granulation significantly influences both the granulation rate and the compressive strength of the granules. When the moisture content of the material is controlled within the range of 16%-20%, the granulation rate and compressive strength of the granules are optimal. Too little moisture results in a low granulation rate; too much moisture causes the material to clump and stick together, resulting in a reduced granulation rate. When the moisture content is too low, the compressive strength of the granules increases with increasing moisture content, which is beneficial for improving the compressive strength of the granules. However, when the moisture content is too high, the excess moisture disrupts the interactions between fertilizer molecules, causing the dried granules to crack and resulting in a decrease in compressive strength. Before using a disc granulator, the optimal moisture content, disc speed, and disc inclination angle should be tested to ensure high fertilizer production line efficiency and high pellet quality. Furthermore, the finer the raw material powder, the better the granulation effect.
Disc granulators are widely used in organic fertilizer production lines and compound fertilizer production lines. Fertilizer production using disc granulators offers low investment, high output, simple process, and intuitive operation, resulting in excellent economic and social benefits.