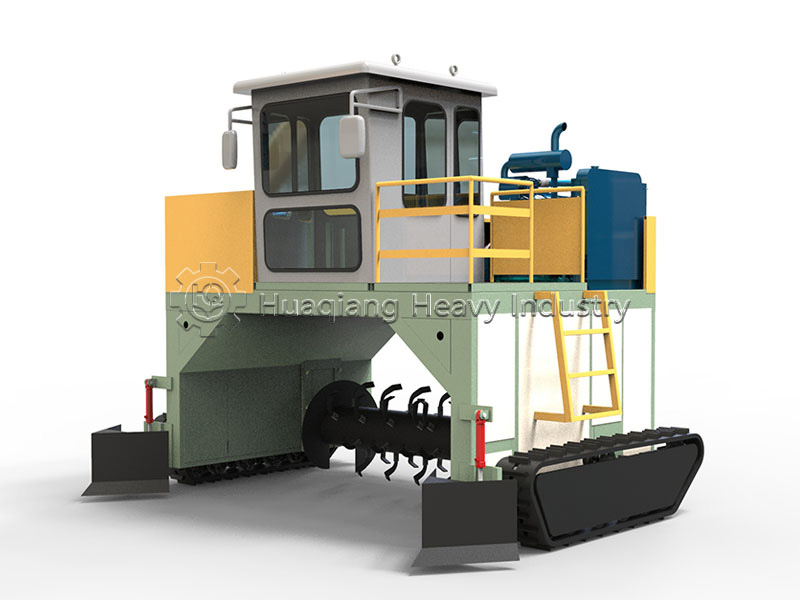
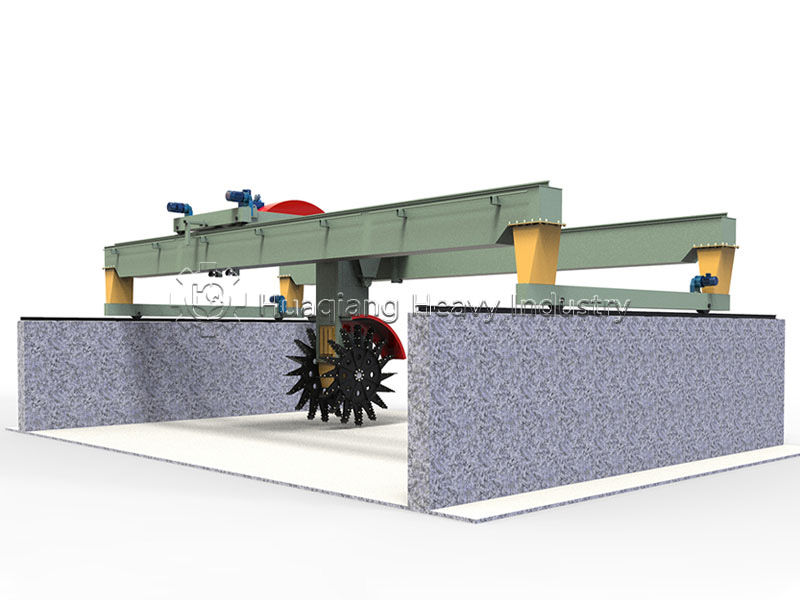
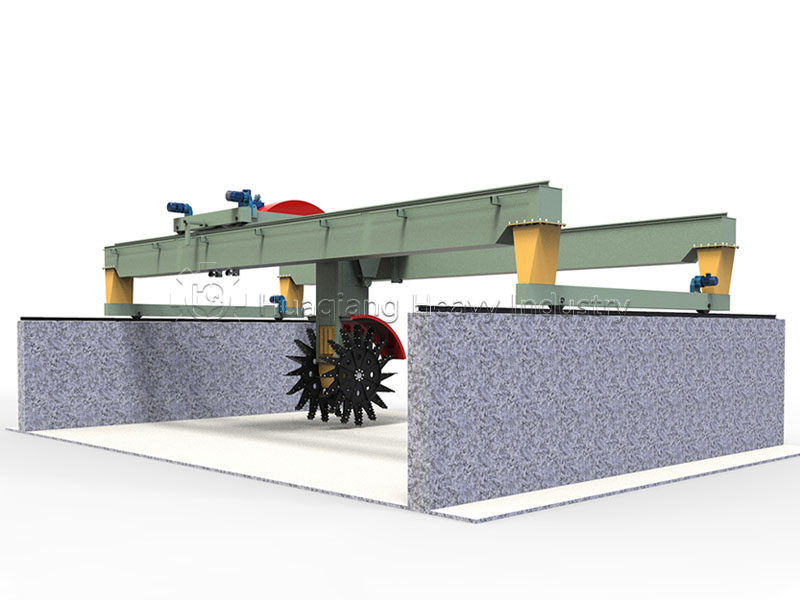
In the context of green agricultural development and the resource utilization of organic waste, the chain compost turning machine has become a core piece of equipment for large-scale organic fertilizer production plants and composting facilities, providing strong support for aerobic fermentation processes.
This equipment is specifically designed for processing organic waste such as livestock manure and crop straw, efficiently addressing the problems of low efficiency and long fermentation cycles associated with traditional composting methods. Compared to simple compost turning machines and hydraulic compost turning machines, the chain compost turning machine, with its unique chain-driven turning mechanism, can penetrate deep into the compost pile, achieving uniform material mixing and significantly improving oxygen supply efficiency, thus accelerating the decomposition and transformation of organic materials.
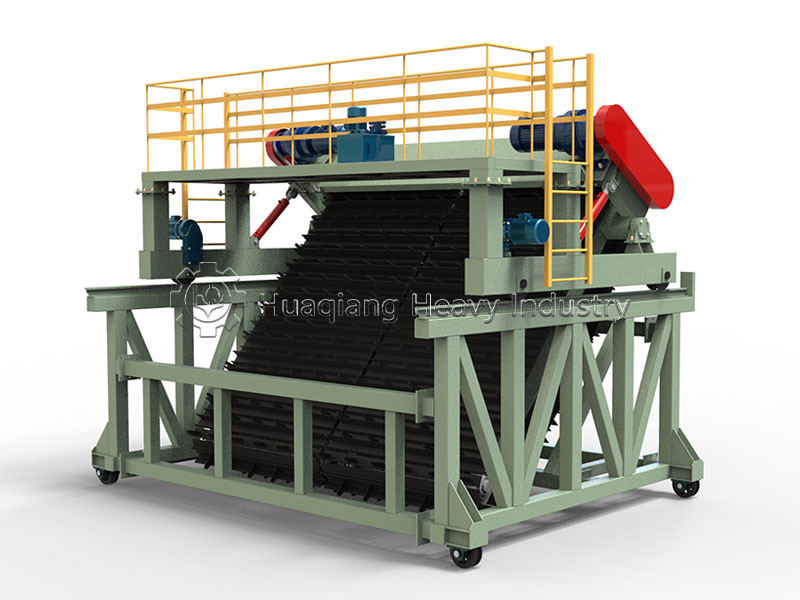

In bio-organic fertilizer production lines, the role of the chain compost turning machine is particularly crucial. Its automated control system can precisely adjust the turning frequency and depth, and with the optional oxygen supply system, it allows organic waste to ferment rapidly under suitable conditions, transforming into high-quality organic fertilizer in just a few weeks. The equipment is also highly adaptable, seamlessly integrating with organic fertilizer production lines and assisting in the environmentally friendly and large-scale operation of agricultural waste treatment projects, reducing pollution while creating economic value.
For companies pursuing efficient production, the advantages of the chain compost turning machine are significant: its durable chain structure is suitable for long-term, high-intensity operation, its flexible walking system can adapt to irregular sites, and its automated operation reduces labor costs. Whether used in conjunction with windrow compost turning machines for multi-scenario operations or independently in large-scale composting projects, it can drive the upgrading of the organic fertilizer industry with its stable performance, injecting momentum into the development of green agriculture.