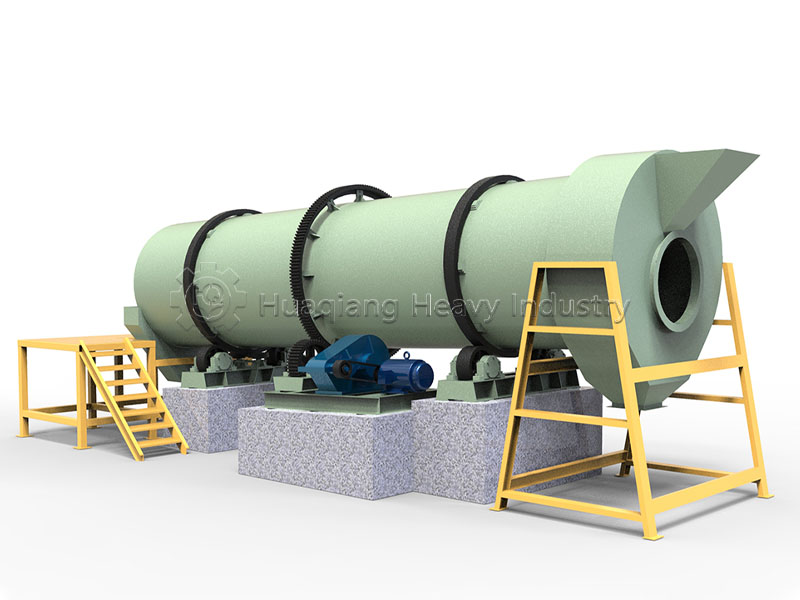
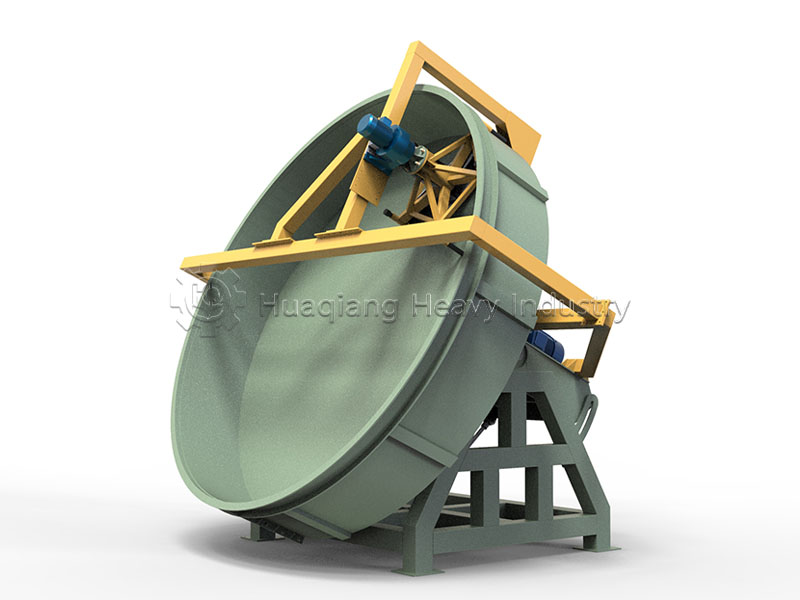
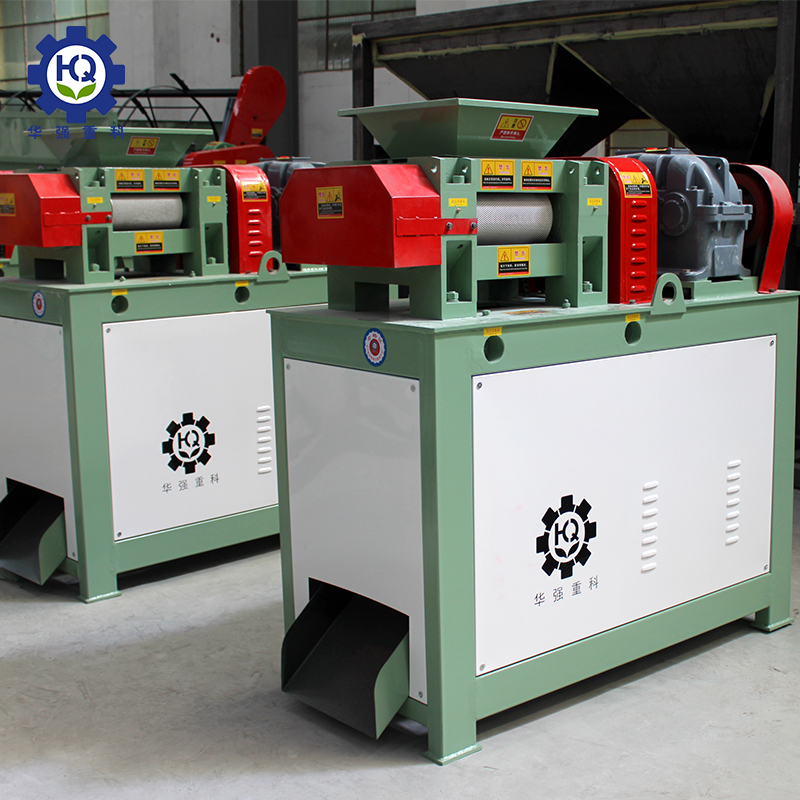
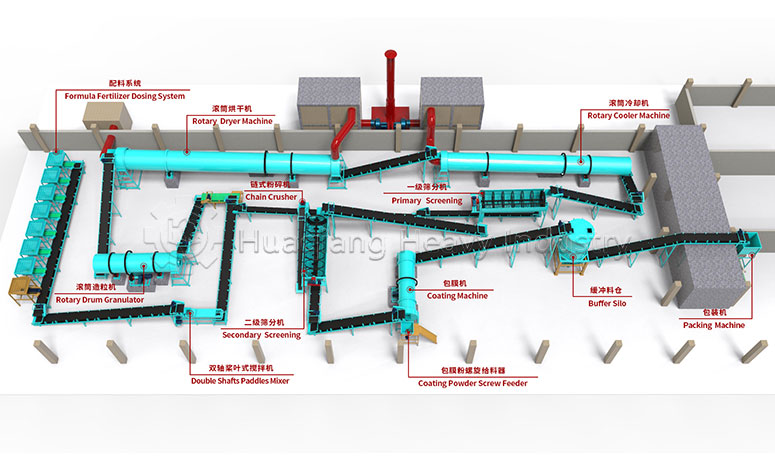
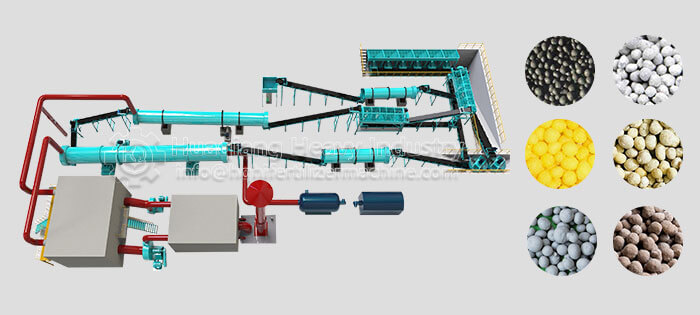
Chlorine is an essential micronutrient for plant growth. Chlorine in fertilizers primarily originates from various chlorine-containing raw materials. After processing by fertilizer granulator machines, it often serves as an important nutrient component in NPK fertilizer production lines. Different types of chlorine have different characteristics, release rates, and functions. Proper selection can fully utilize the nutritional value of chlorine.
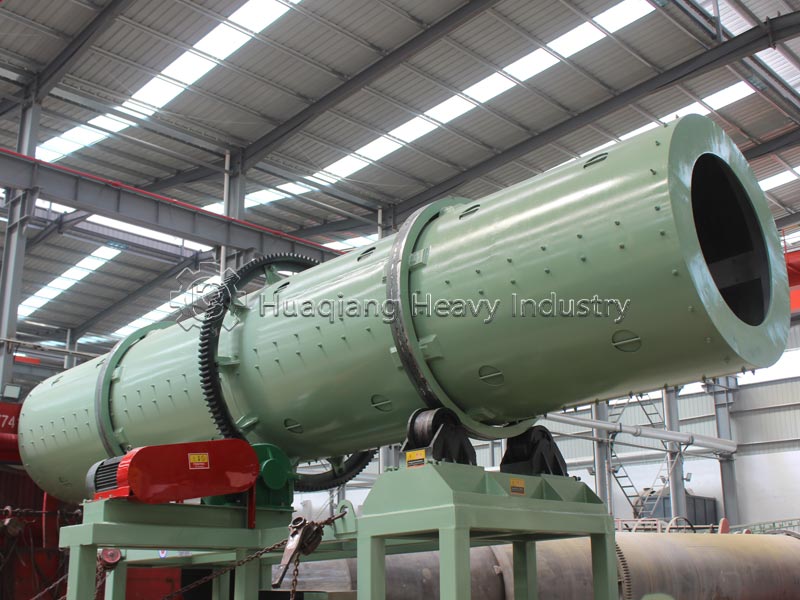
Chlorine in potassium chloride is the most common type. Processed and shaped by rotary drum granulator machines, it has a high chlorine content and is released quickly, making it easily absorbed by crops. Combined with potassium, it regulates cell osmotic pressure, promotes the transport of photosynthetic products, and strengthens crops’ resistance to lodging and drought. It is suitable for chlorine-loving crops such as corn and rice, providing both chlorine and potassium.
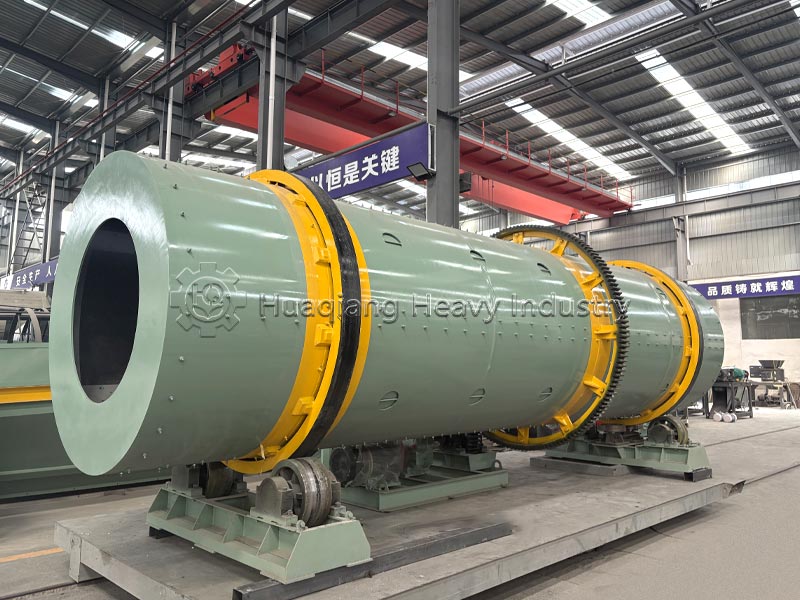

Chlorine in ammonium chloride is a nitrogen-chlorine synergistic type, also providing nitrogen. Chlorine promotes root development, improves nitrogen absorption efficiency, inhibits soil pathogens, and reduces diseases. It is suitable for crops such as wheat and cotton, and is ideal for medium-fertility soils, providing both nitrogen and chlorine.
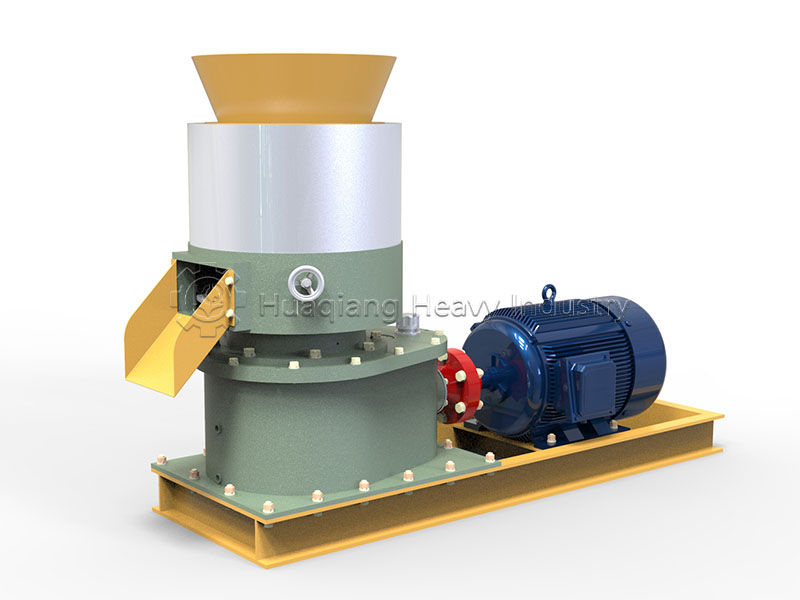
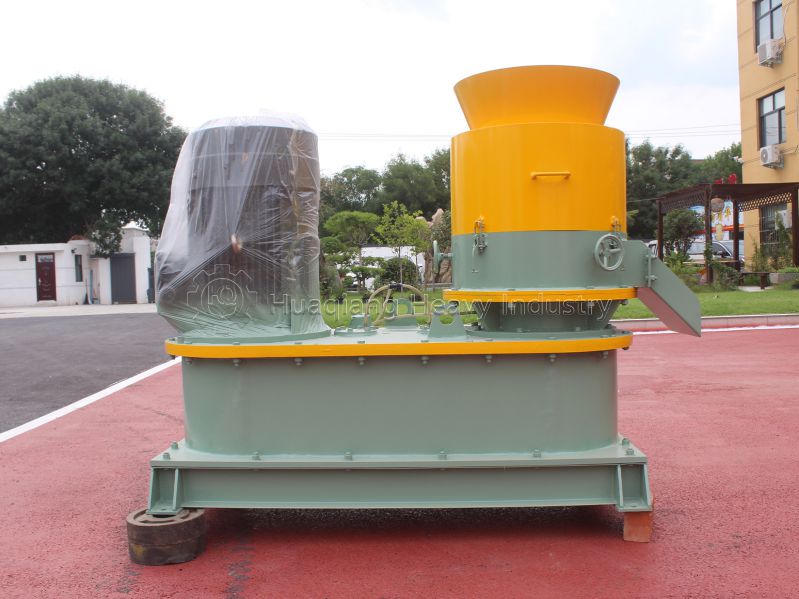
Chlorine in chlorine-containing compound fertilizers is in a complex form and is a common component of NPK fertilizer production lines. After processing by fertilizer granulation machines, it works synergistically with nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, providing a slow and sustained release of nutrients. It can help improve the utilization rate of other nutrients and is suitable for large-scale, diversified crop cultivation, balancing growth and quality.
In summary, the main types of chlorine in fertilizers are potassium chloride, ammonium chloride, and complex forms. By utilizing NPK fertilizer production lines and considering crop and soil conditions, the nutritional benefits of chlorine can be fully realized, contributing to efficient agricultural production.