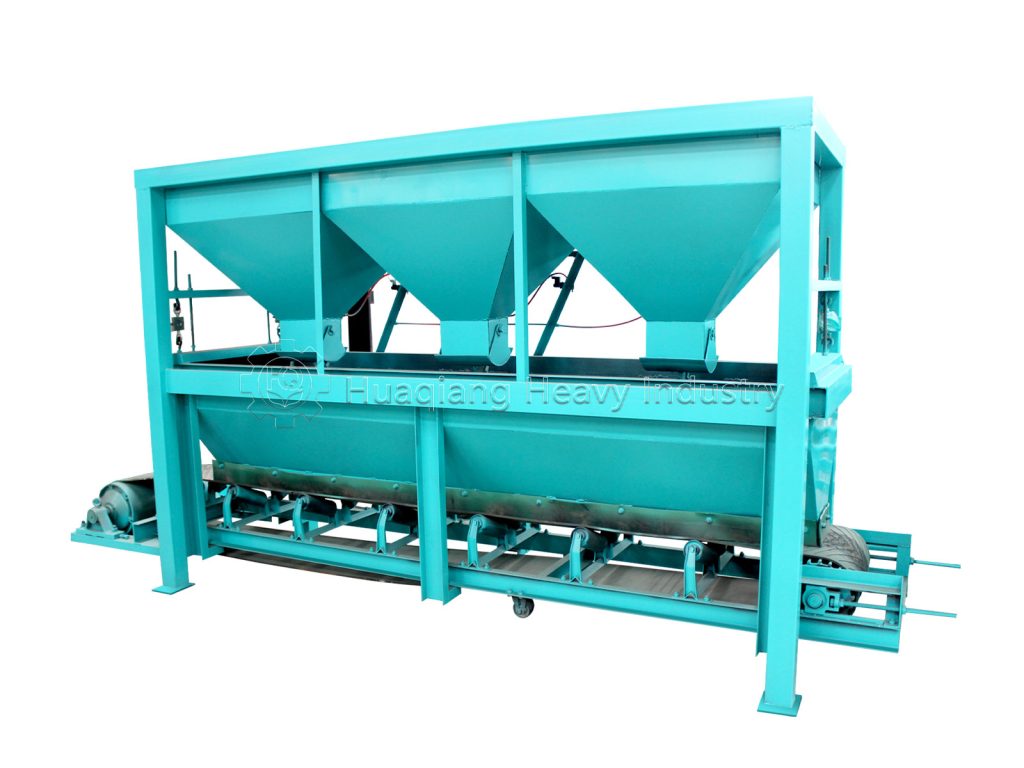
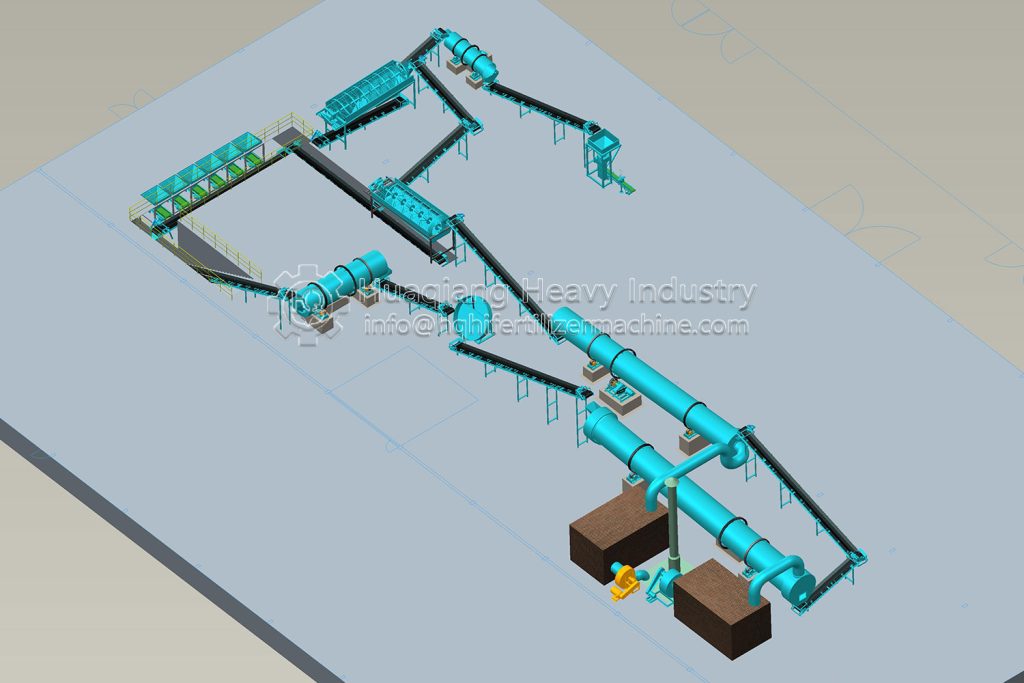
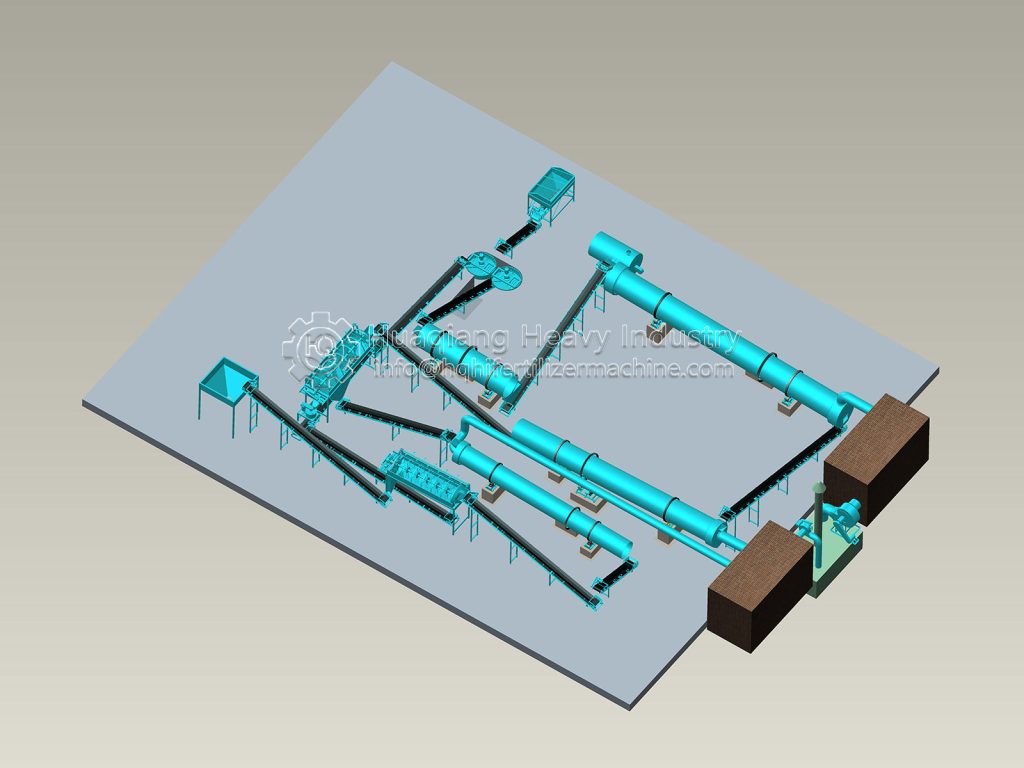
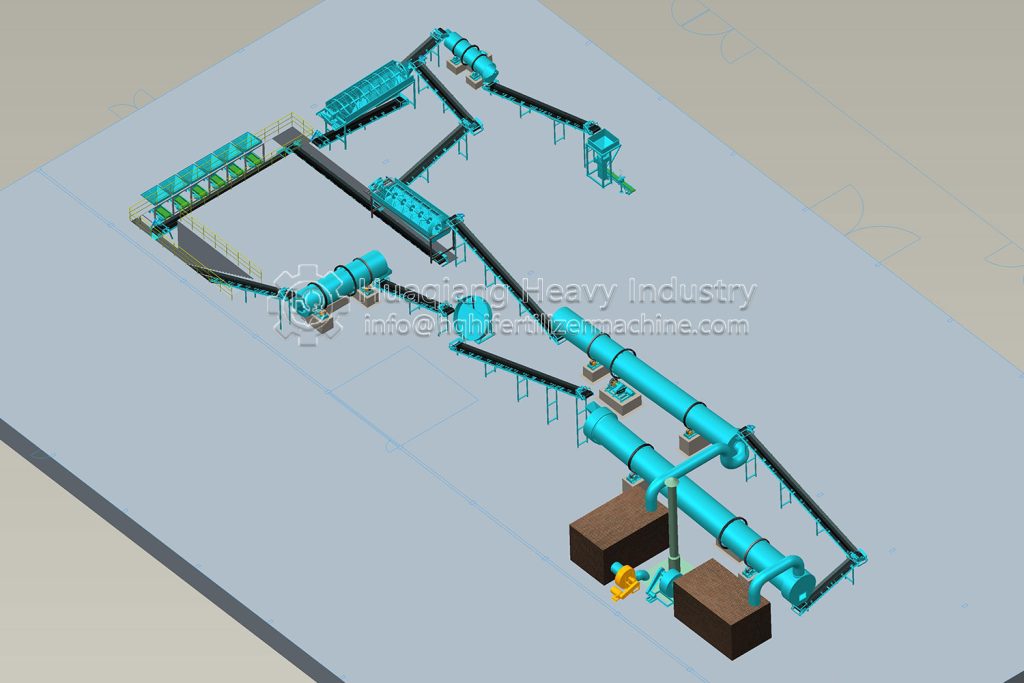
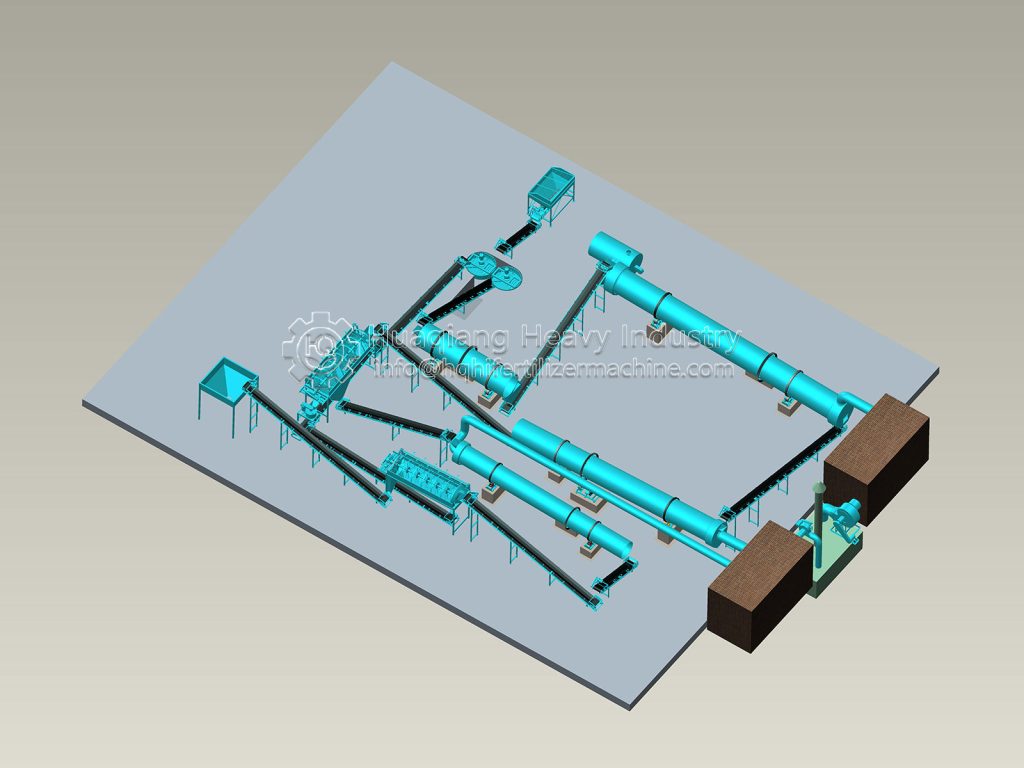
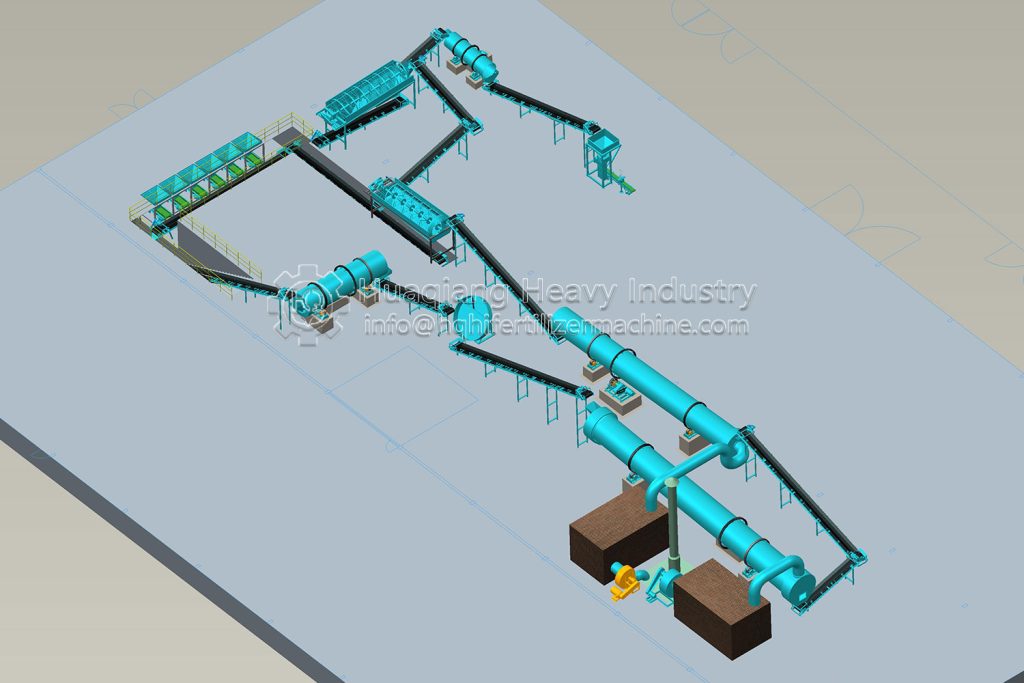
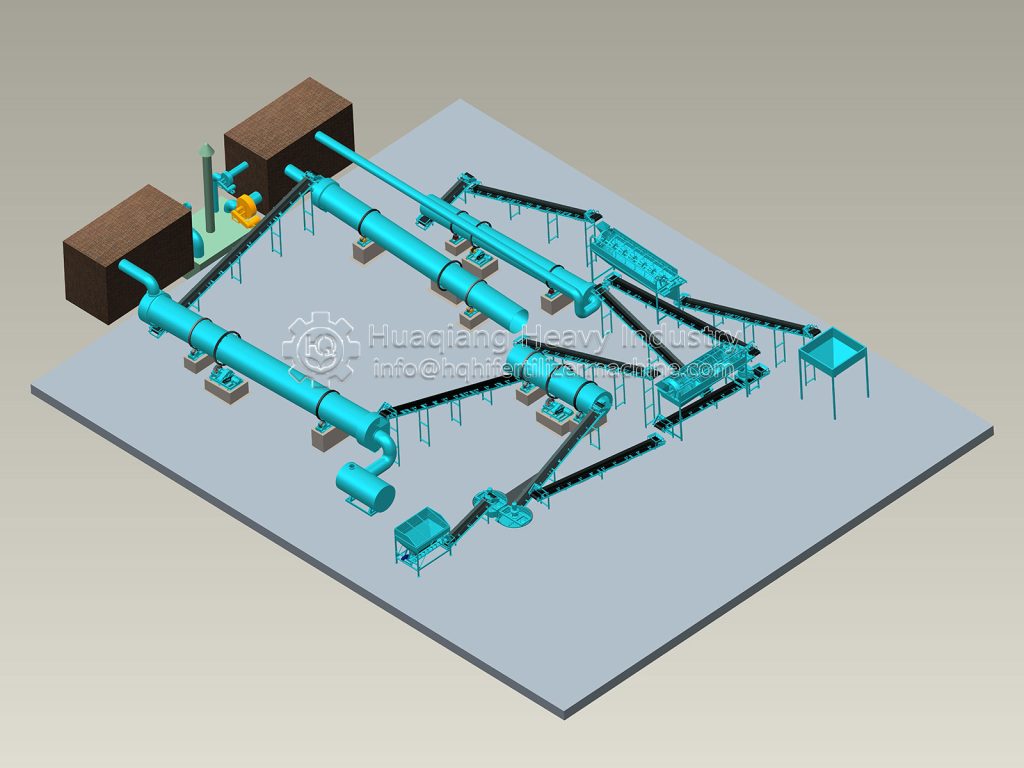
In the entire operation of bio-organic fertilizer equipment, the fertilizer mixer machine, seemingly a “basic link,” is actually a “hidden hero” that determines the final fertilizer effect and production efficiency.
The core objective of bio-organic fertilizer equipment is to transform organic waste such as straw and livestock manure into ecological fertilizer rich in beneficial bacteria through harmless treatment. The uniformity of raw material mixing directly affects the fermentation effect and nutrient balance. The fertilizer mixer machine perfectly addresses this key requirement: through the rotational action of its multi-dimensional mixing structure, it breaks down the physical differences between raw materials, achieving uniformity in carbon-nitrogen ratio, humidity, and microbial distribution across the entire process.

The mechanical mixing of the fertilizer mixer machine ensures that every component of the raw material is fully in contact. This not only provides a “homogeneous substrate” for the fermentation stage of the bio-organic fertilizer equipment but also allows microbial agents to adhere evenly to the organic materials, significantly improving microbial activity and composting efficiency, and shortening the fermentation cycle.
As the “quality gatekeeper” in bio-organic fertilizer equipment, the fertilizer mixer machine ensures the nutrient balance and fermentation quality of ecological fertilizer through precise mixing, making every step of the transformation of organic waste into high-quality fertilizer more controllable and efficient, and providing solid support for the large-scale development of green agriculture.