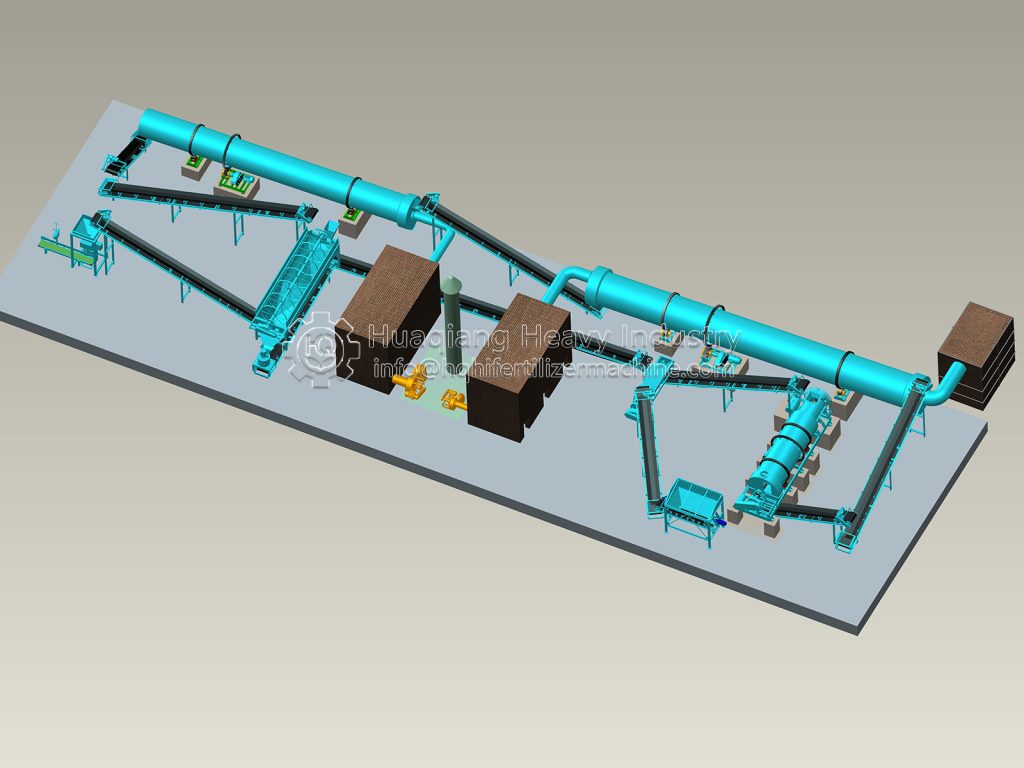
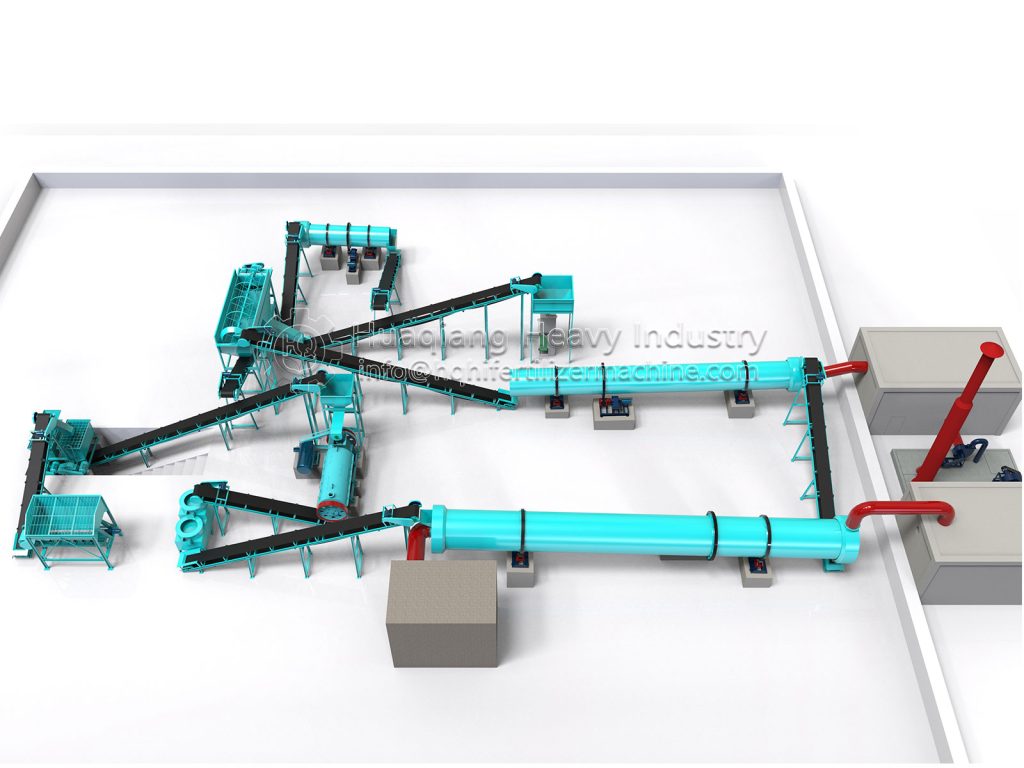
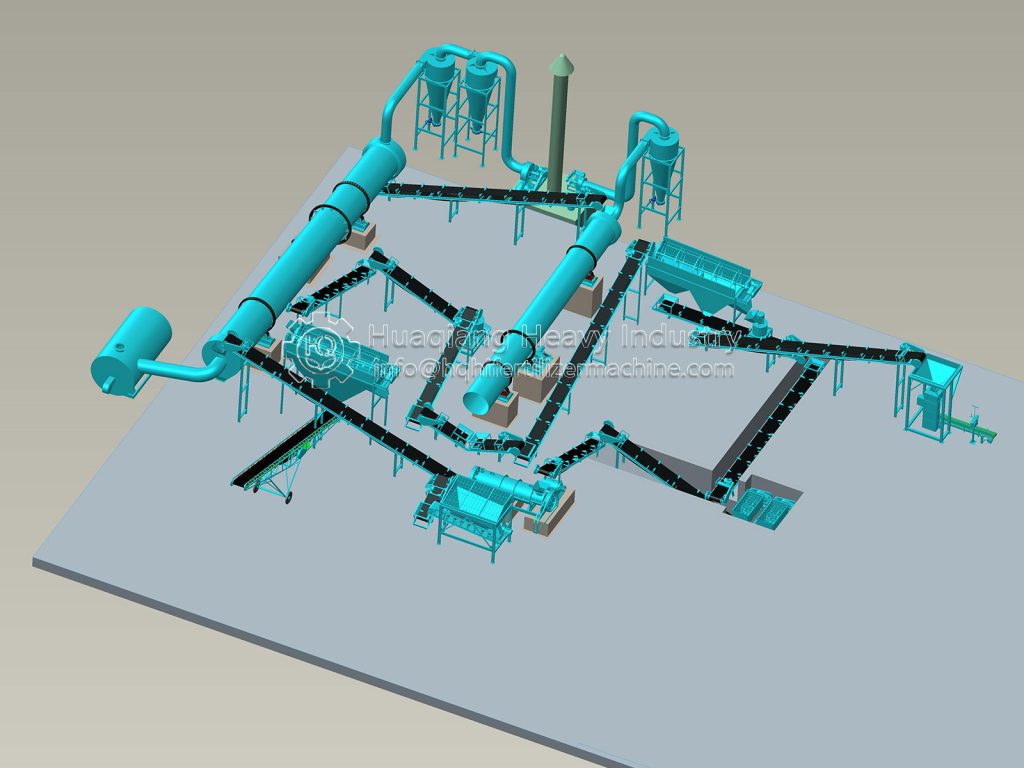
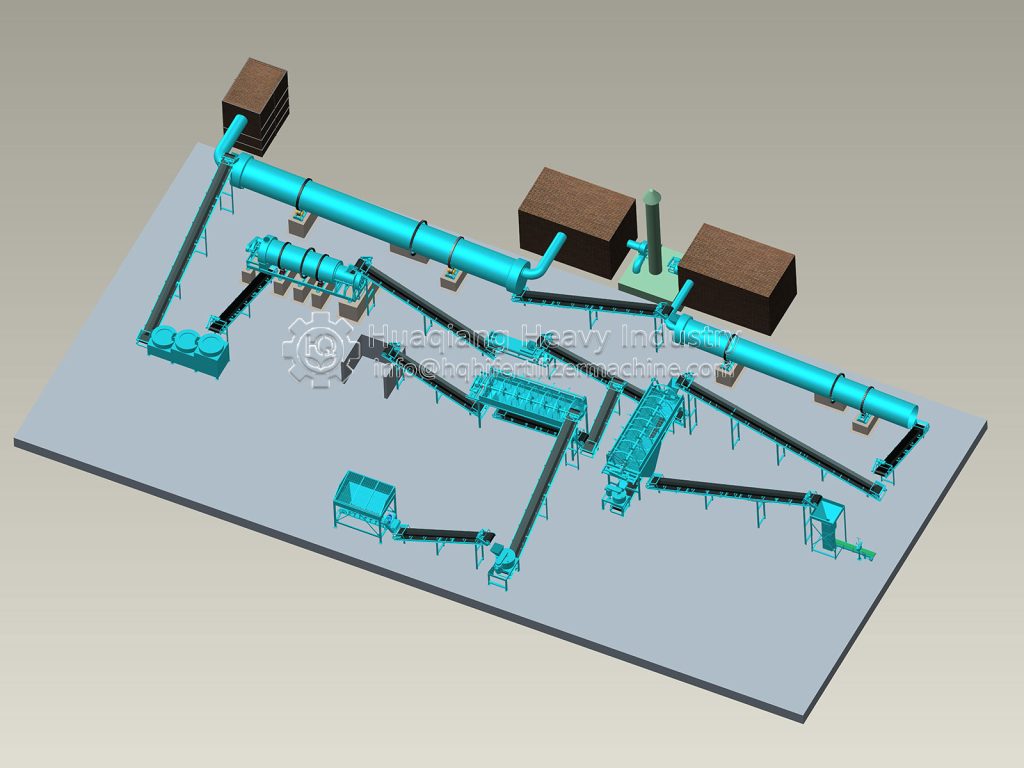
As a key component of the agricultural circular economy, the stable operation of the organic fertilizer production line directly impacts agricultural product quality and environmental safety. This contingency plan has been developed to effectively address various risks in the production process and ensure continuous and efficient operation of the production line.
Raw material supply risk is the primary challenge facing the production line. Organic fertilizer raw materials are primarily agricultural waste, such as livestock and poultry manure and straw. These are susceptible to seasonal fluctuations, epidemics, and other factors, leading to supply disruptions or substandard quality. To address this, it is necessary to establish records for at least three raw material suppliers, sign long-term supply agreements, clearly define raw material quality standards, and establish an emergency replenishment mechanism. Furthermore, a raw material storage area with a capacity of at least 15 days should be reserved within the plant, equipped with rainproof and anti-seepage facilities to prevent mold and loss of raw materials.
Equipment failure directly impacts production schedules. Sudden failure of core equipment in the organic fertilizer production line, such as the fermentation turner, granulator, and dryer, will result in a complete shutdown. A regular equipment inspection system should be established, with daily checks on the operating status of key components and weekly comprehensive maintenance. A spare parts warehouse should be established to stockpile vulnerable parts such as motors and bearings, ensuring replacement within two hours of a malfunction. Emergency maintenance agreements should be signed with equipment manufacturers, promising on-site response within 48 hours for major malfunctions.
Production safety risks cannot be ignored. The fermentation process of raw materials may produce flammable and explosive gases such as methane, and the drying process presents a fire hazard. Combustible gas detectors and alarms should be installed in the fermentation workshop, and automatic fire extinguishing systems should be installed in the drying section. Regular fire safety training and emergency drills should be conducted to ensure that every operator is proficient in the use of fire extinguishing equipment. A strict hot work approval system should be implemented, and supervisors and fire extinguishing equipment must be present on-site.
Furthermore, external risks such as market fluctuations and policy adjustments must be addressed. Diversified product sales channels should be established, and changes in agricultural subsidy policies should be closely monitored to adjust production plans in a timely manner. By establishing a comprehensive risk prevention and control system, the impact of various risks on organic fertilizer production lines can be effectively reduced, ensuring the stability of the green agricultural development industry chain.