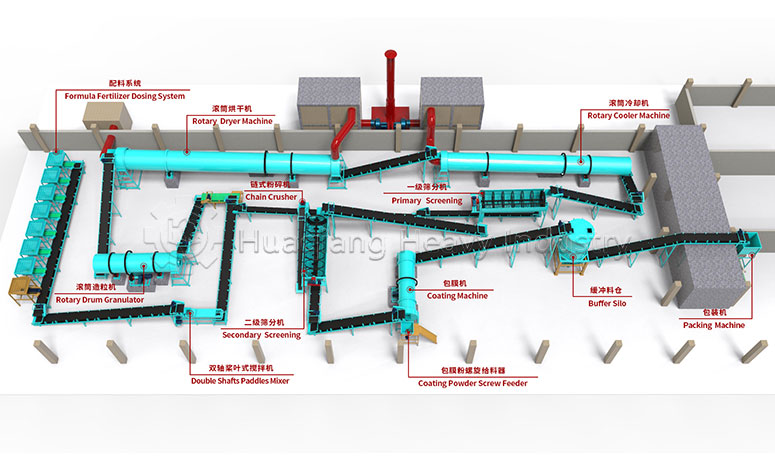
Organic fertilizers commonly come in powder, granular, and pellet forms. The core difference in their production lies in the molding process and equipment adaptation. The choice can be made flexibly based on planting needs, balancing efficiency and fertilizer effectiveness.
Powdered organic fertilizer: The simplest to produce, suitable for broadcasting. Composted materials (chicken manure, straw, etc.) are crushed and screened to remove impurities, requiring no molding step. Large-scale production can utilize mixing equipment in an organic fertilizer production line to adjust nutrients and then directly package the product. It is suitable for base fertilization in large fields and greenhouses, offering quick results and low cost.
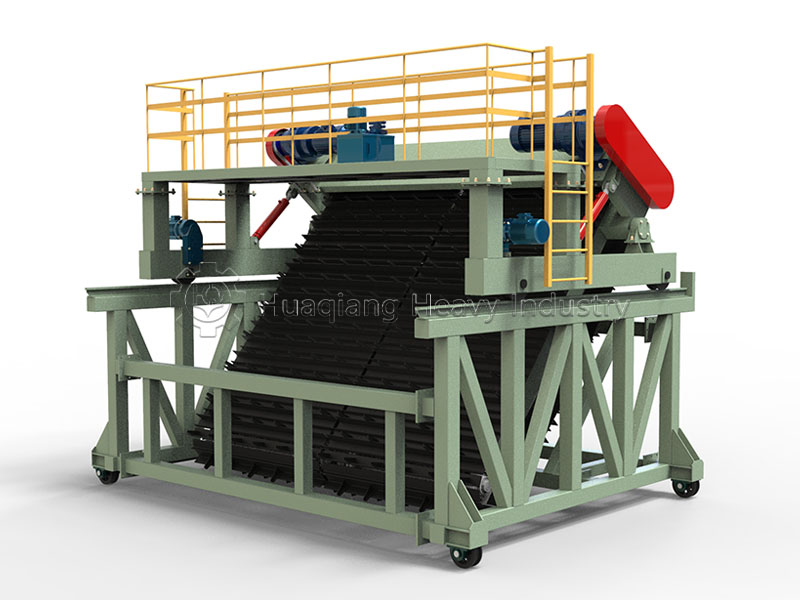
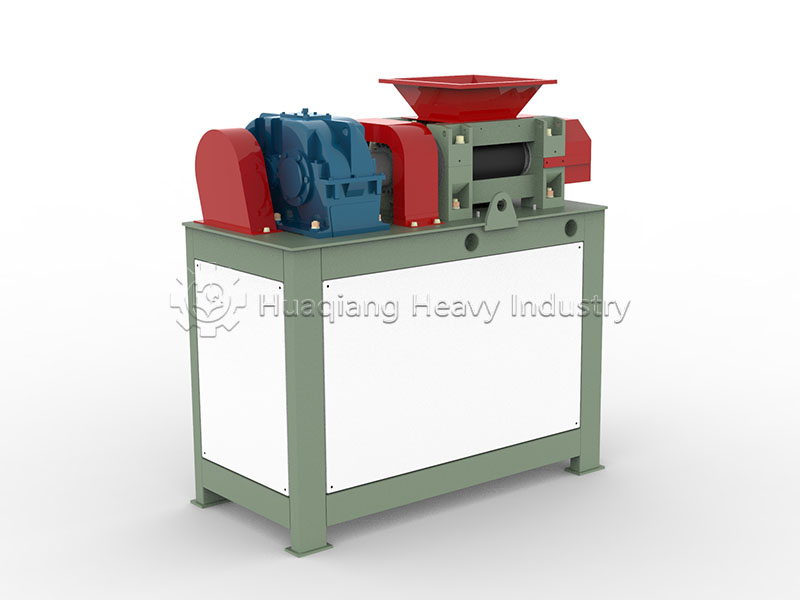
Granular organic fertilizer: Suitable for mechanized application and convenient for storage and transportation. After crushing and screening the composted material, the moisture content is adjusted to 55%-60%, and then fed into a double roller press granulator for molding. After drying, cooling, and secondary screening, it is packaged. Small-scale composting can use small granulation equipment, while large-scale production can be integrated into an organic fertilizer production line. It is suitable for top dressing of fruit trees and vegetables, as it is less prone to caking and allows for even application.
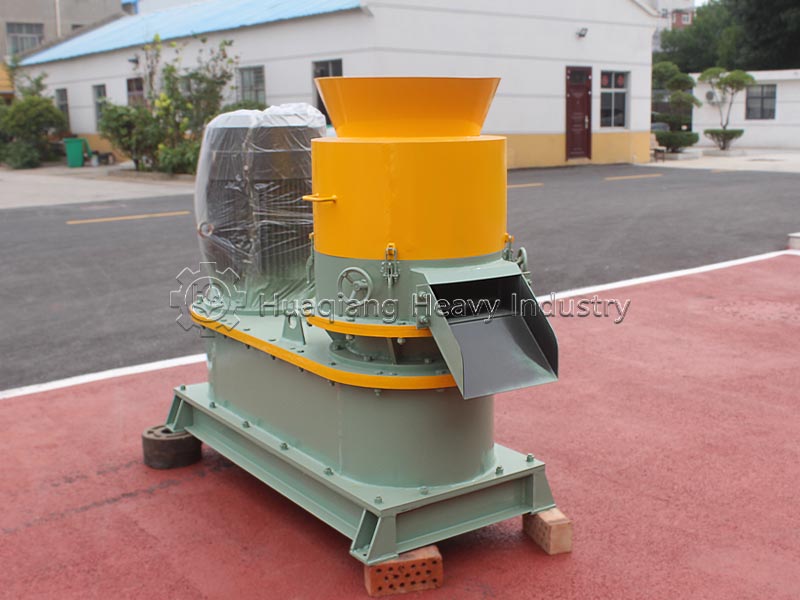

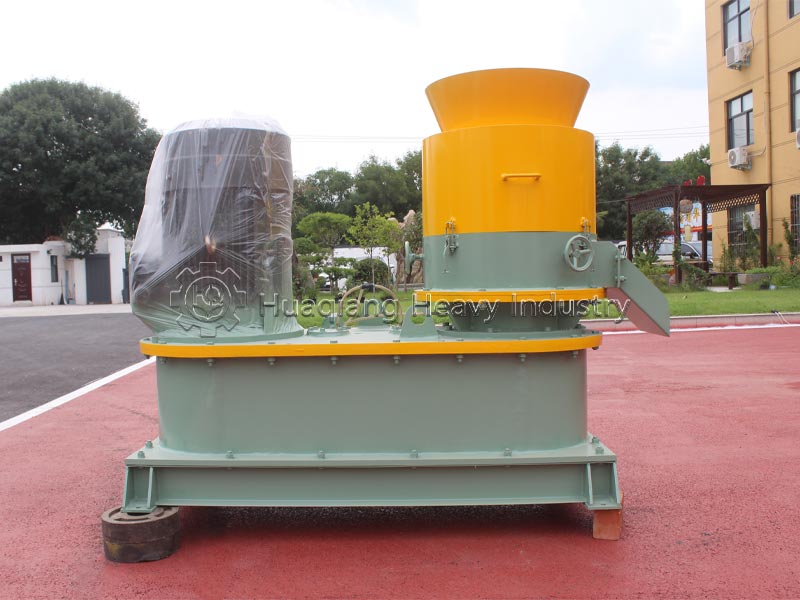
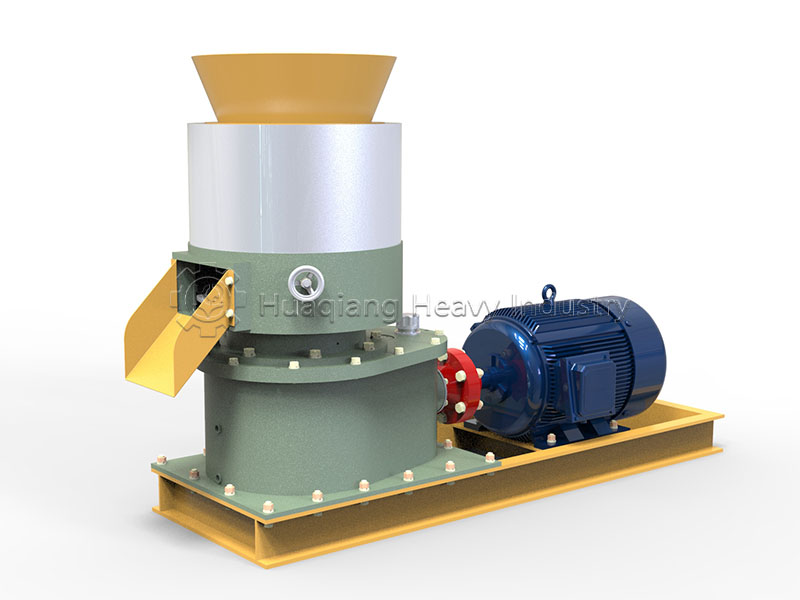
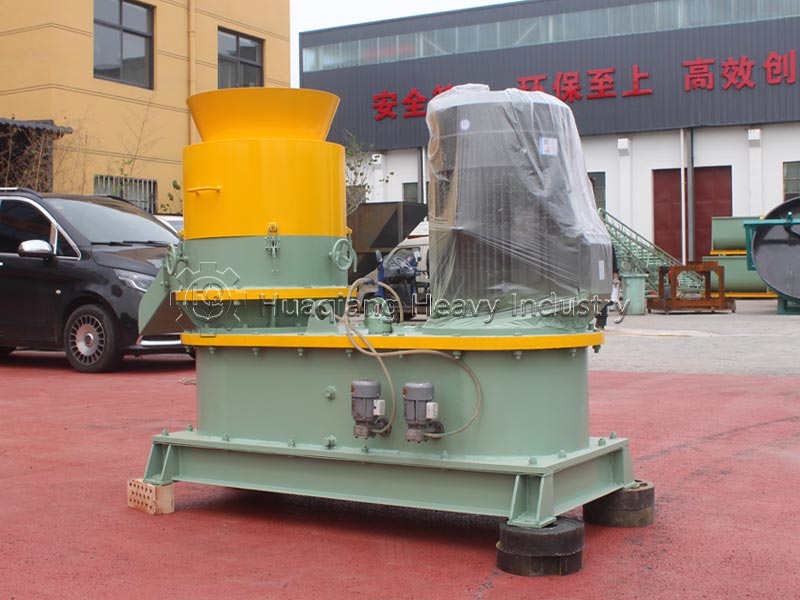
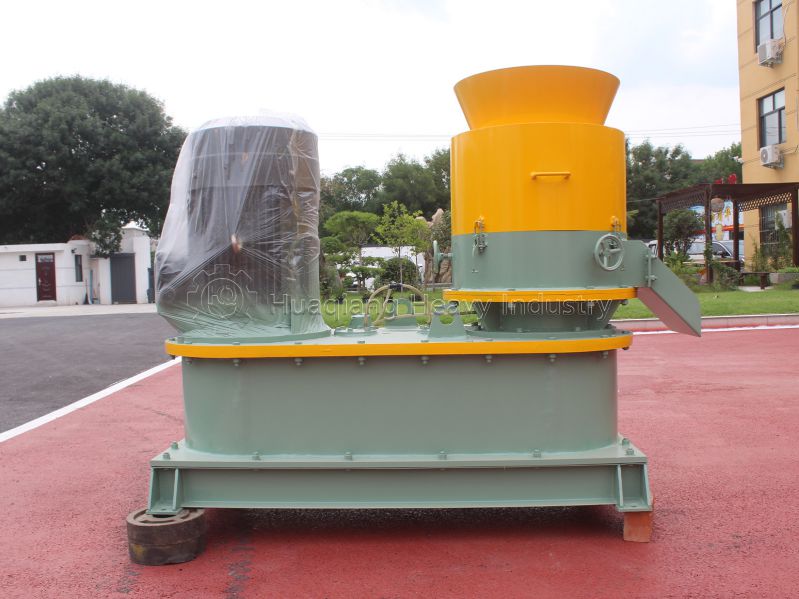
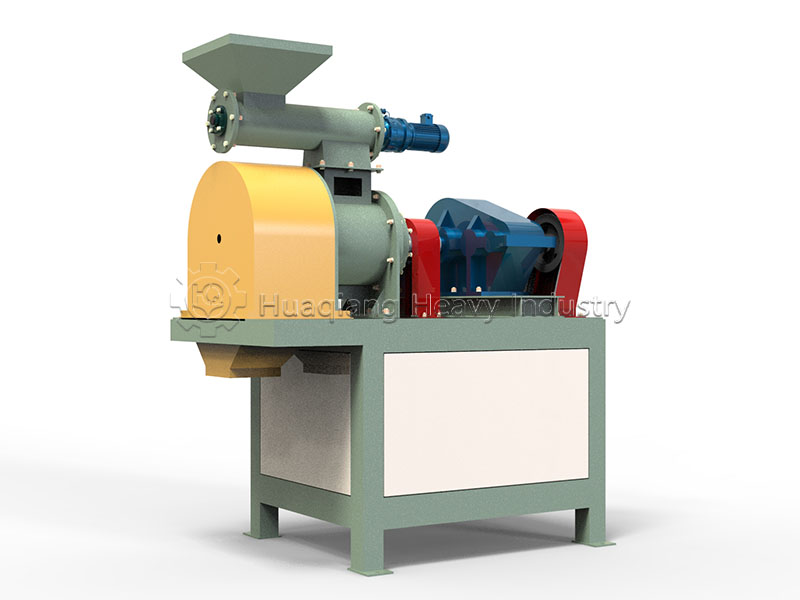
Pellet organic fertilizer: Suitable for hole application and furrow application. A flat die pelleting machine is used to extrude the pre-treated composted material (a small amount of binder can be added) into pellets, which are then cut, dried, and cooled. It has high density and long-lasting fertilizer effect, suitable for hole application in fruit trees and seedlings, reducing nutrient loss.
In summary, the core of producing different shapes of organic fertilizers is “standardized composting + appropriate molding.” Powdered fertilizer focuses on crushing and screening, while granular and pellet fertilizers rely on granulation equipment. Choosing the appropriate form based on needs can improve application convenience and maximize fertilizer effectiveness.