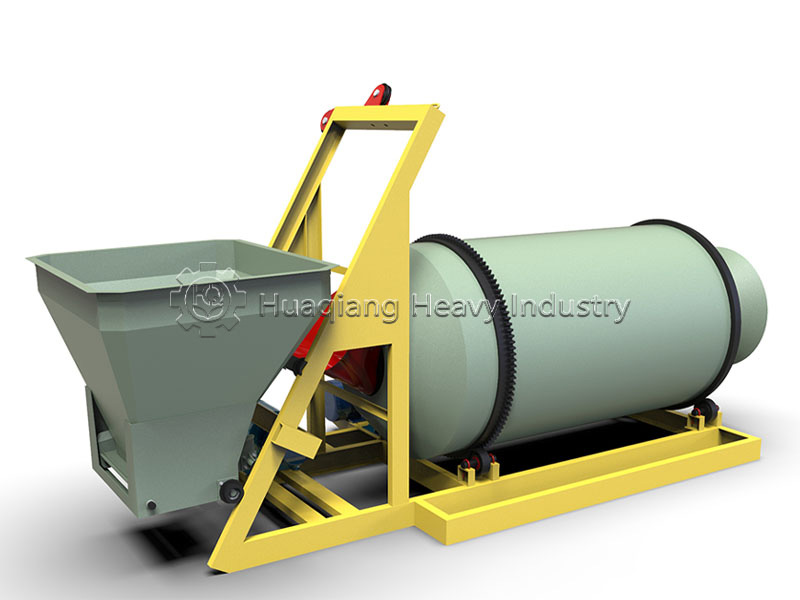
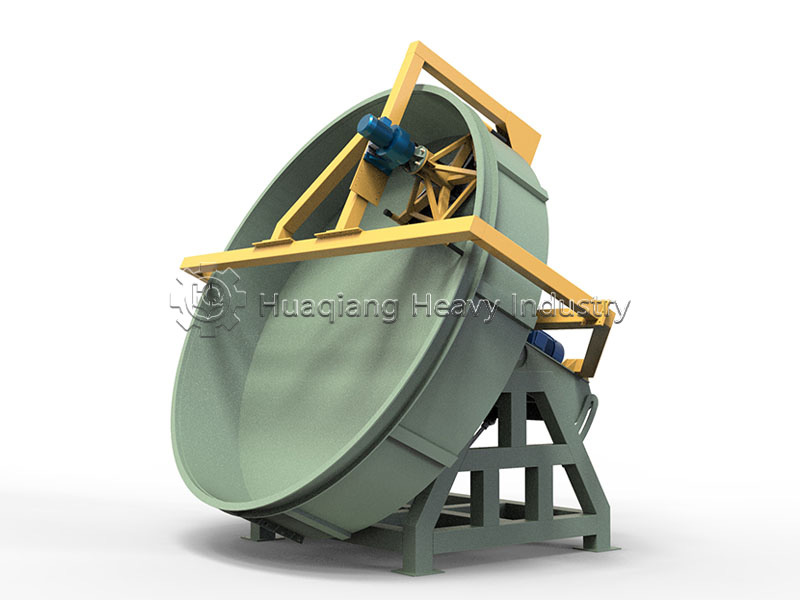
The core of NPK blended fertilizer’s market competitiveness lies in nutrient uniformity and granule stability. Achieving these two key indicators depends on precise control of the two crucial stages in the NPK blending fertilizer production line: blending and granulation. NPK blending machines and BB fertilizer mixers are responsible for establishing the foundation of nutrient uniformity, while NPK fertilizer granulators ensure granule formation quality. Together, they form the quality assurance system of the production line.
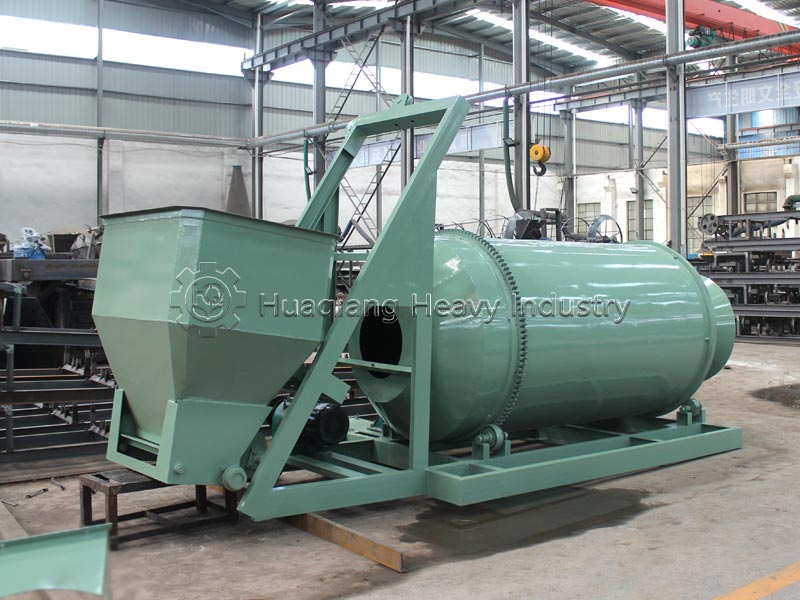
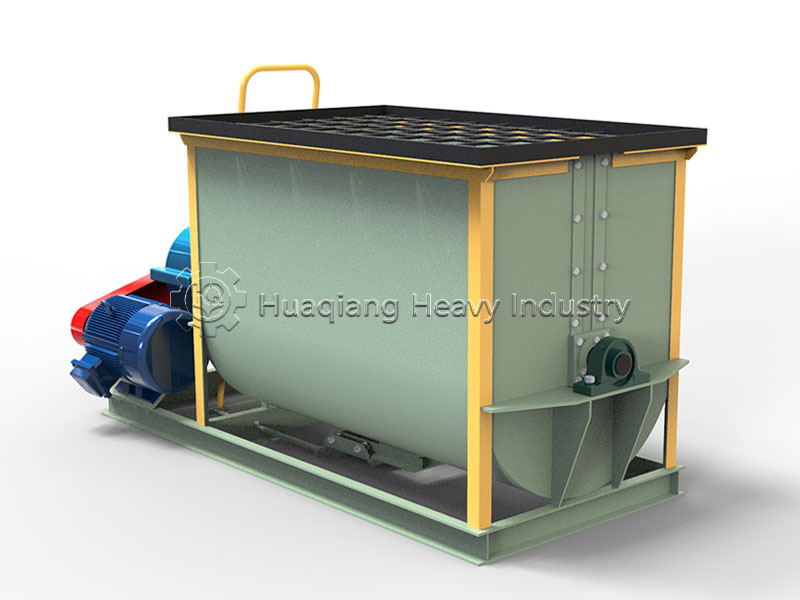
The blending stage is the “first line of defense” for nutrient uniformity. NPK blending machines and BB fertilizer mixers need to be selected according to production needs. For large-scale continuous production, NPK blending machines, with their large capacity and high speed, can achieve rapid and uniform mixing of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and trace elements; small and medium-sized production lines or multi-batch, small-volume production are better suited to BB fertilizer mixers, which are flexible in operation and easy to adjust, allowing for quick switching between different formulation schemes, and the mixing uniformity meets conventional production requirements. Regardless of the equipment used, the principle of “fine materials first, then coarse materials, and layered feeding” must be strictly followed to avoid material segregation affecting uniformity.
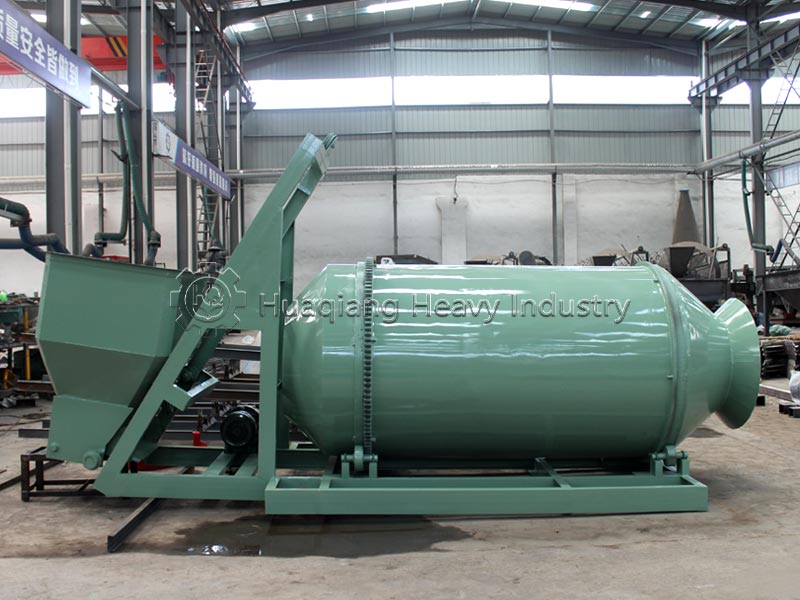

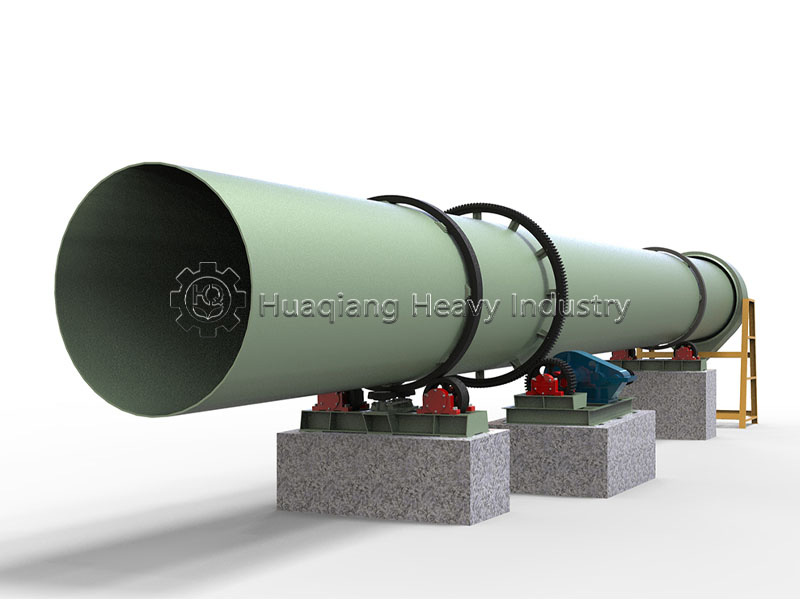
The granulation stage determines the final quality of the granules. The NPK fertilizer granulator needs to be precisely matched with the blending effect of the preceding stage. After the uniformly blended materials enter the granulator, the granulation speed and pressure need to be adjusted according to the material’s moisture content and particle size characteristics to ensure that the produced granules meet the strength standards and have uniform particle size. If the blending in the preceding stage is uneven, even with precise granulation parameters, fluctuations in nutrient content of the granules will occur.