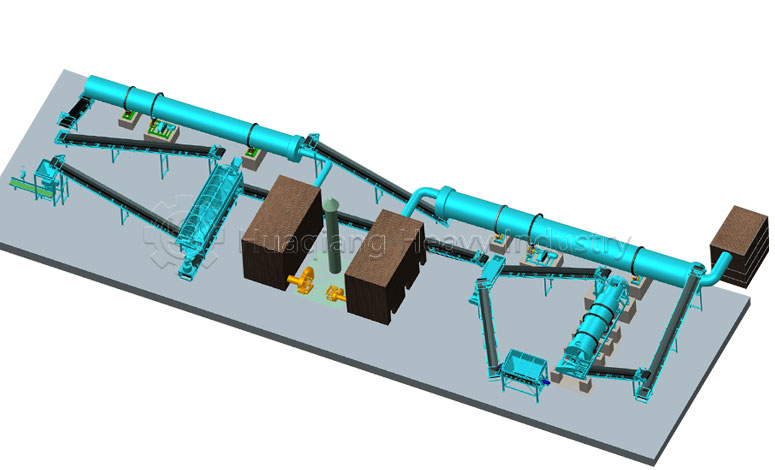
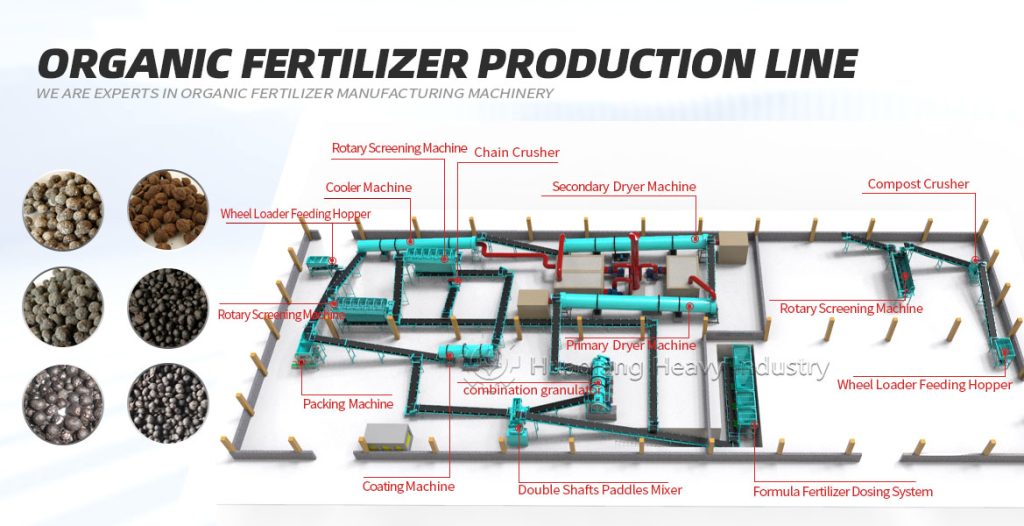
In large-scale organic fertilizer production, the organic fertilizer production line, compost turner, and fertilizer compaction machine are indispensable. Their synergistic operation is the core support for achieving standardized and efficient organic fertilizer production, ensuring both production efficiency and improved product quality.
The organic fertilizer production line is the central hub, connecting all stages from raw material pretreatment, fermentation, granulation, and packaging. It achieves standardized processing of raw materials such as livestock manure and straw into organic fertilizer, ensuring smooth transitions between processes and laying the foundation for subsequent equipment operation.
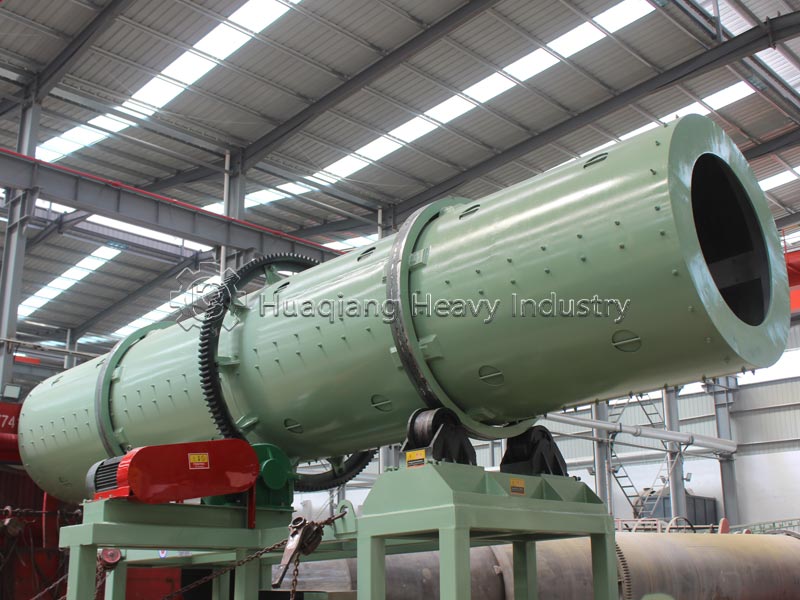
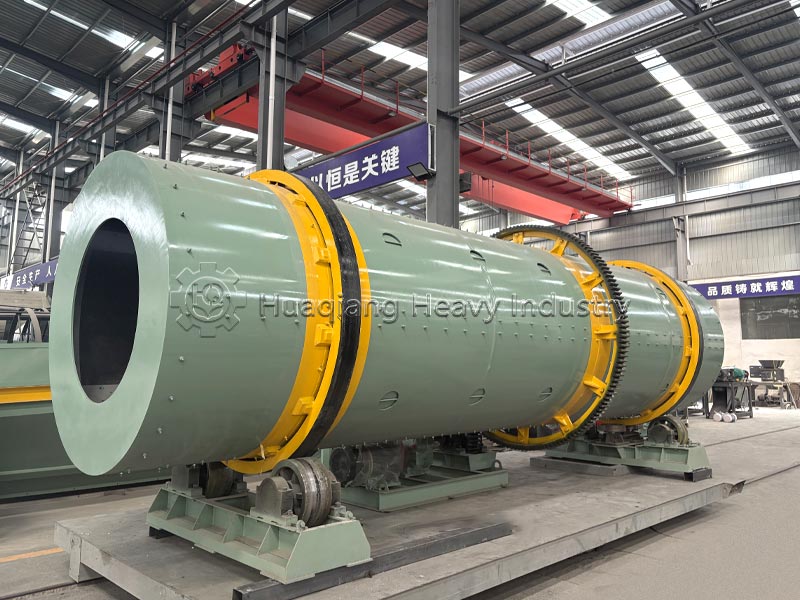
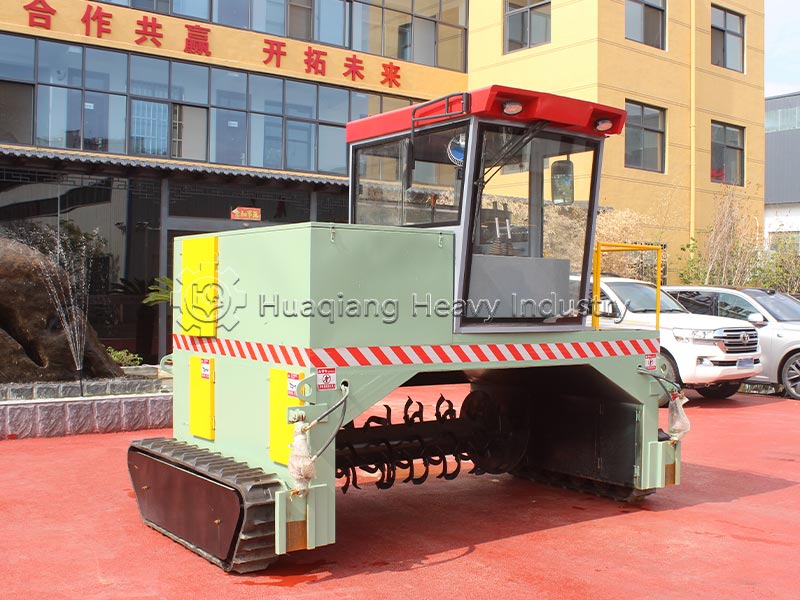
The organic fertilizer compost turning machine is crucial for fermentation, directly determining the quality of compost maturation. During the fermentation stage of the production line, it regularly turns the compost pile, replenishing oxygen, regulating temperature, preventing anaerobic fermentation and foul odors, accelerating maturation, killing pathogens and insect eggs, and ensuring even nutrient distribution, preparing for granulation.
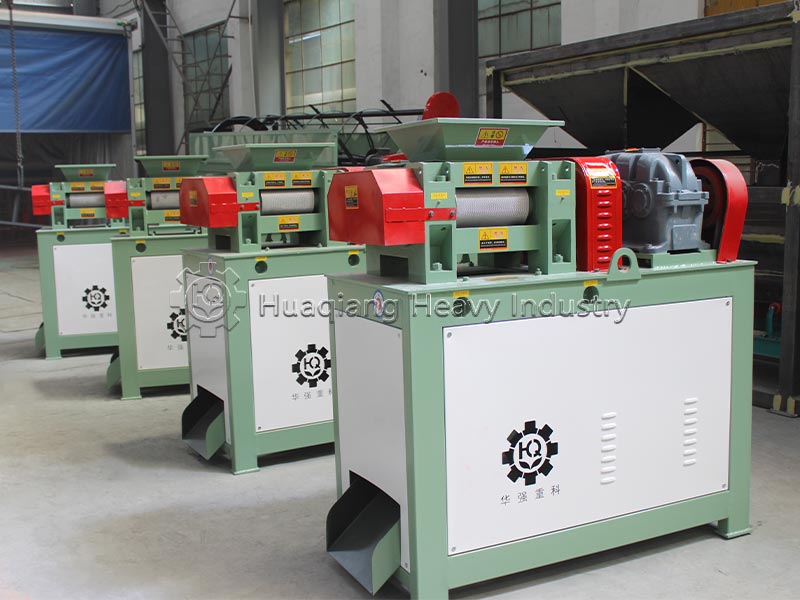

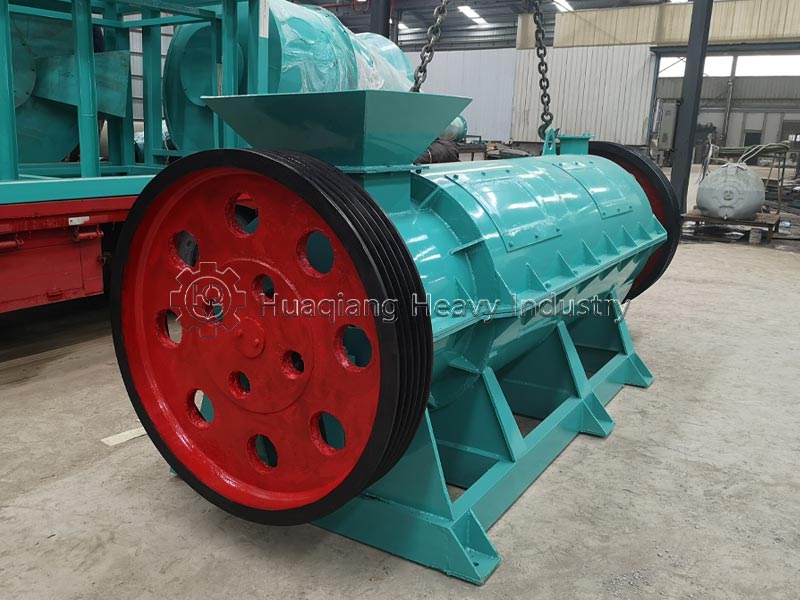
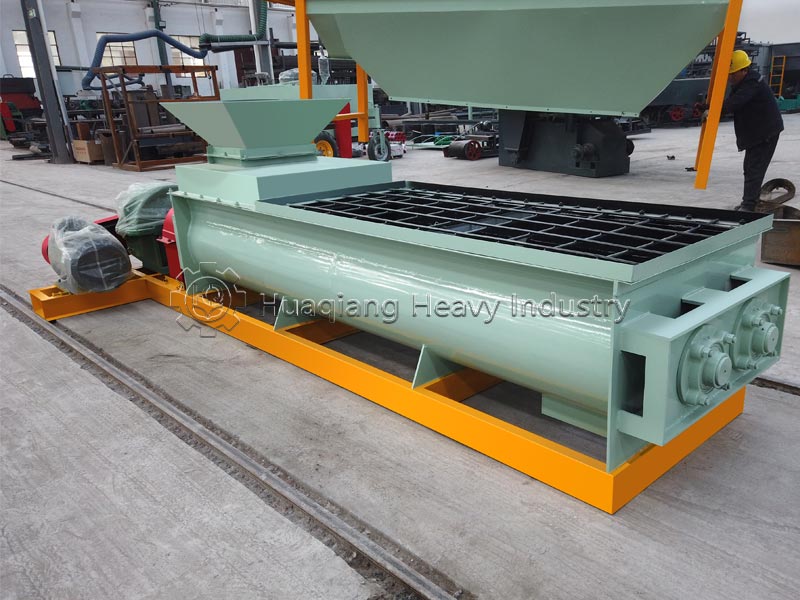
The fertilizer compaction machine is the core of the granulation process. It receives fermented and decomposed raw materials and, through extrusion molding, transforms the loose materials into regular granular organic fertilizer. This improves storage and transportation convenience, controls granule size, ensures more stable nutrient release, and is suitable for various planting scenarios.
The three components work together, with the production line coordinating the overall process. The compost turner ensures the quality of decomposition, and the compactor optimizes the finished product shape. This reduces labor costs, makes production more efficient and the quality more stable, and facilitates large-scale green planting, maximizing the resource utilization of waste.